ELA 7 Grammar Review Part 1: subjects, subject complements
advertisement

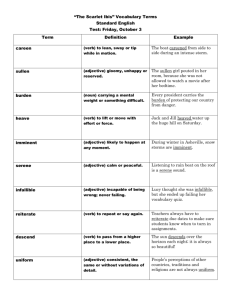
ELA 7 Grammar Review Part 1: subjects, subject complements, direct objects, indirect objects, and object of prepositions. The subject of a sentence is the person or thing doing the action or being described. Examples: George ate the pie. Sam enjoys playing volleyball. The subject of a sentence is one of the basic parts of a sentence. The other basic part is the predicate. The predicate tells us something about the subject (i.e., it tells us what action the subject is performing, or it describes the subject). Every sentence must have a verb, and every verb must have a subject. A subject complement is the adjective, noun, or pronoun that follows a linking verb. The following verbs are true linking verbs: any form of the verb be [am, is, are, was, were, has been, are being, might have been, etc.], become, and seem. These true linking verbs are always linking verbs. Examples: Jack is a gifted athlete. (Jack = subject) (athlete = noun as subject complement) It was he who caught the winning touchdown Friday night. (It = subject) (was = linking verb) (he = pronoun as subject complement) Direct objects can be nouns, pronouns, phrases, or clauses. If you can identify the subject and verb in a sentence, then finding the direct object—if one exists—is easy. Just remember this simple formula: Subject + Verb + what? or who? = Direct Object Examples: Summer and Libby played soccer with a grapefruit pulled from a backyard tree. Summer, Libby = subjects; played = verb. Summer, Libby played what? Soccer = direct object. How to Find the Indirect Object Before you can find the indirect object, you have to find the direct object. You can find the direct object by finding the verb and asking what?. Once you've found the direct object, ask who or what received it? For example: She gave the beggar a gold coin. (Step 1. Find the verb = gave) (Step 2. Ask What? = a gold coin) (Therefore, the direct object is a gold coin.) (Step 3. Ask Who (or what) received it? = the beggar) (Therefore, the indirect object is the beggar.) The object of a preposition is the noun or pronoun governed by a preposition. The object of a preposition is usually (but not always) the noun or pronoun immediately to the right of the preposition. Example: Are those biscuits on the table for the dogs? Part II: Adjectives Refer to the Adjective Power Point attached to the classroom website to answer the following questions. What is a descriptive adjective? Give an example of a descriptive adjective as well as the word it modifies. What is a demonstrative adjective? Provide an example. What is an interrogative adjective? Provide an example. What is an indefinite adjective? Provide an example. What is a superlative adjective? Provide THREE examples. Part III Prepositions (this will be completed together in class) What does a prepositional phrase include? How can you determine if a word is being used a preposition or an adverb? Give an example for each. How do you identify an adjective phrase? Provide an example.