DECISION MAKING - Future Academy
advertisement
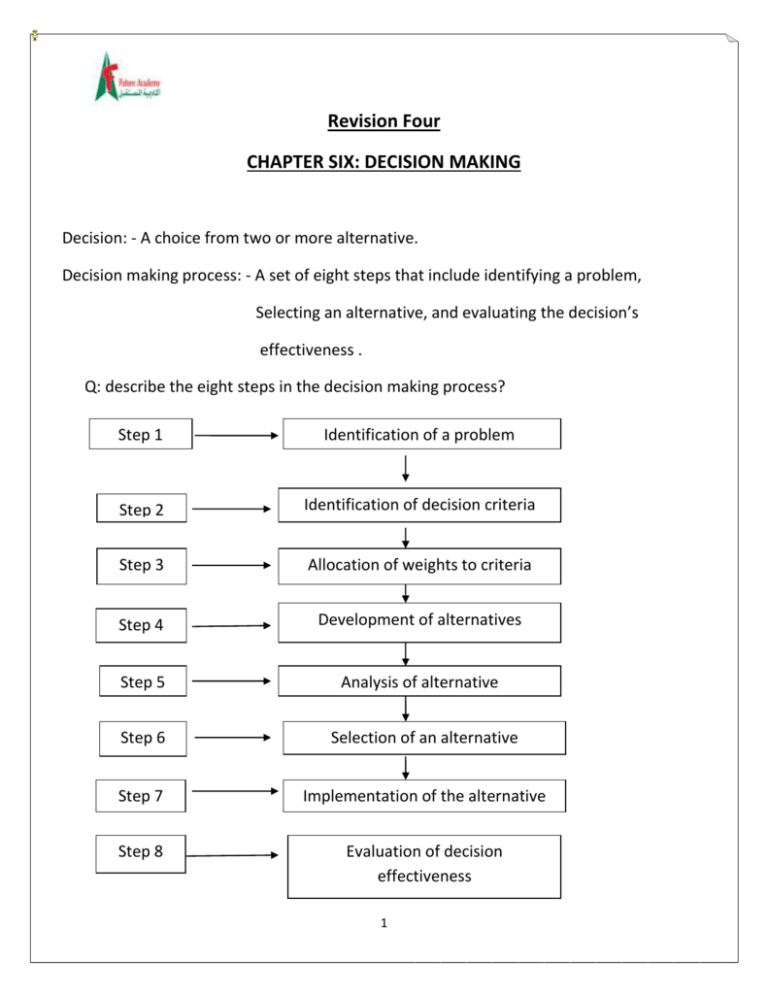
Revision Four CHAPTER SIX: DECISION MAKING Decision: - A choice from two or more alternative. Decision making process: - A set of eight steps that include identifying a problem, Selecting an alternative, and evaluating the decision’s effectiveness . Q: describe the eight steps in the decision making process? Step 1 Identification of a problem Step 2 Identification of decision criteria Step 3 Allocation of weights to criteria Step 4 Development of alternatives Step 5 Analysis of alternative Step 6 Selection of an alternative Step 7 Implementation of the alternative Step 8 Evaluation of decision effectiveness 1 Mark (true) or (false) 1. The last step in the decision making process is to evaluate the input of the decision (false) Correction: - The last step in the decision making process is to evaluate the output of the decision 2. Decision is choosing among alternatives (true). 3. The decision maker must weigh the items to give them the correct priority (true) 4. Selecting is choosing the worst alternative ( false ) 5. . Implementing normally comes before selecting the alternative (false) Correction: - selecting the alternative comes before implementing the alternative 6. If the problem still exists the manager would need to assess what went wrong (true) 7. Decision making is a part of all four managerial functions (true). Q: what’s a problem? Problem: the difference between an existing & a desired a state of affairs Q: what are the three characteristics of a problem? 1. Be aware of the problem 2. Being under pressure to act. 3. Having the resources needed to take action. Q: How can managers be aware of a problem? By making comparison between the actual conditions and the desired conditions Q; where might problem come from ? Deadlines, financial crises, customer complains, competitor actions, organizational polices. 2 Mark (true) or (false) 1. Problem identification is subjective (true). 2. Managers needn’t be aware of the problems (false). 3. A problem without pressure can be postponed (true). 4. Managers must have resources and authority to solve problems(true ) Q: How are decisions made? Rationality: - decisions are made in the best interest of the organization. Bounded rationality: - decisions are made rationally, but decision makers are limited by their ability to process information so they end up satisficing. Assumptions are that decision makers - Will not seek out or have knowledge of all alternatives - Will satisfice – choose the first alternative that solves the problem – rather than maximize the outcome of their decision by considering all alternatives and choosing the best . Decision making may be strongly influenced by organization’s culture, internal politics, power considerations & escalation of commitment. Intuition :- Making decisions on the basis of experiences ,feelings & accumulated judgments. Mark (true) or (false) 1. Rational decision making means accepting solutions that are good Enough (false) Correction:-rational decision making means decisions are made in the best interest of the organization. 2. Managers are always rational (false). 3 3. Making decisions rationally will minimize the likelihood of achieving the goal (false). 4. Under bounded rationality managers satisfice rather than maximize(true) 5. satisfice means accepting solutions that are good enough (true ). 6. Intuitive decision making based on experiences and feelings (true). 7. Many managers are using their intuition to make decisions (true). Q: what are the two types of problems? Structured problems: Involve goals that clear Are familiar (have occurred before ) Are easily and completely defined – information about the problem is available & complete. Example: - A customer’s returning a purchase to a store. Unstructured problems: Are new & unusual with incomplete information. Problems that will require custom- made solutions. Q: What are the types of decisions? Programmed decision: - a repetitive decision that can be handled by a routine approach. Types of programmed decisions Policy: - a general guideline for making a decision about a structured problem. Rule: - a statement that limits what a manager or employee can or cannot do in carrying out the steps involved in a procedure. Procedure: - a series of interrelated steps that a manager can use to respond (applying a policy) to a structured problem. 4 Example: Policy: - accept all customer-returned merchandise Rules: - managers must approve all refunds over $50.00 Procedure:- follow all steps for completing merchandise return documentation . Nonprogrammed : decision that are unique & nonrecurring Decision that generate unique responses. Mark (true)or(false) 1. Policy is in contrast to rule (true)(give reason ) Answer: A policy establishes general parameters for the decision maker rather than specifically starting what should or should not be done. 2. Managers in all levels and in all areas of organizations make decisions (true). 3. Depending on the type of the problem the manager can use different types of decisions.(true) 4. Middle and lower level managers make decisions about the organization’s goals and new markets to move into (false). Correction: - top managers make decisions about the organization’s goals and new markets to move into. 5. Unusual problems need custom-made solutions(true) 6. Top Managers make dozens of routine decisions (false) Correction:-top managers make nonprogrammed decisions 5 Q: What are the three conditions may managers faces when they make decisions? Certainty :An ideal situation in which a manager can make an accurate decision because the outcomes of every alternative choice is known. Risk :A situation in which the manager is able to estimate the likelihood (probability) of outcomes that results from the choice of particular alternatives. Uncertainty :Limited or information prevents estimation of outcome probabilities for alternatives associated with the problem & may force managers to rely on intuition Managers do face decision making situations of uncertainty - Under these conditions ,the choice of alternatives is influenced by the limited amount of information available to the decision maker &by the psychological orientation of the decision maker - The optimistic manager’s choice to maximize the maximum payoff (Maximax) - The pessimistic manager’s choice to maximize the minimum payoff (maximin) Mark (true) or (false) 1. When the outcome of every alternative is known managers make their decisions under the risk condition (false) Correction: - certain condition 2. The optimistic decision maker maximax choice (true) 6 7