Transition Fact Sheet - Moore Public Schools
advertisement

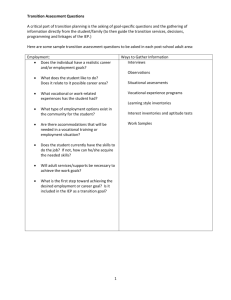
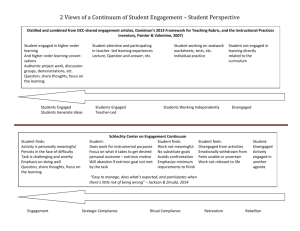
Transition Fact Sheet Under IDEA 2004, IEPs must include transition services for the child by age 16. The transition plan should reflect the student’s interests, preferences, accomplishments and skills, what they need to learn, and what they want to do. Person-centered planning is a way to identify goals and develop plans to accomplish goals. Self-Advocacy/ Self-Determination training: • Students who passed more than half or all courses in 8 curriculum areas (remedial academics, traditional content classes, personal finance, community access, behaving responsibly, goal-setting or problem solving, specialized vocational education, regular vocational education) were more likely to be engaged in post-school education (Halpern et al., 1995) • Students with higher self-determination skills were more likely be engaged in post-school employment (Wehmeyer & Schwartz, 1997) Predicts improved outcomes in: Education and Employment Transition Curriculum: • Students who participated in the Youth Transition Program with four or more transition goals met were more likely to be engaged in post-school employment or education Benz, M., Yovanoff, P., & Doren, B. (1997). • Students who received transition planning services during high school were more likely to be engaged in post-school education (Halpern et al., 1995) Predicts improved outcomes in: Education and Employment Student Lead IEPs: Students have the ability to advocate for themselves and don’t have to rely on case-manager as much. More Parental participation in the IEP meetings increased substantially. Students gain confidence and communication skills through leading IEP meetings. Students who have Student-led IEPs find it easier to apply self-advocacy skills in college or on the job. (Mason, McGahee-Kovac, and Johnson 2004) Predicts improved outcomes in: Education and Employment *** Fellow MPS teachers who focus on transition skills training report taking significantly less time to deal with student, teacher and parent complaints. References: Benz, M., Yovanoff, P., & Doren, B. (1997). School-to-work components that predict postschool success for students with and without disabilities. Exceptional Children, 63(2), 155-165