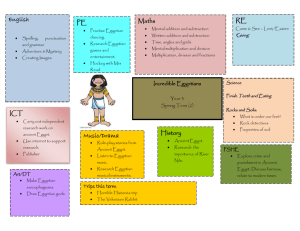
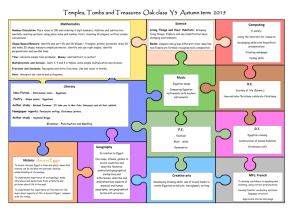
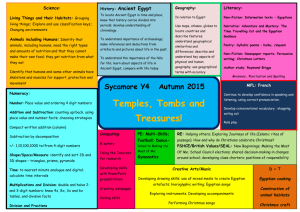
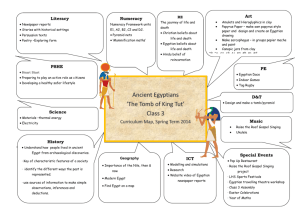
Hieroglyphs Lesson Plan
advertisement

Tennessee Tech University How to Write Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphs Name: Sherri Wade Date: March 8, 2013 Lesson Title: Egyptian Symbols: Learning How to Write Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphs in a 21st Century Grade/Level: 6th grade Curriculum Standards State/Common Core Curriculum Standards Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will explore these elements of society to develop an appreciation and respect for the variety of human cultures. Learning Expectations: 1.05 Understand the role that diverse cultures and historical experiences had on the development of the world. 1.06 Understand the influence of science and technology on the development of culture through time. 6.1.05 Understand the role that diverse cultures and historical experiences had on the development of the world. a. Explain and give examples of how language, literature, the arts, architecture, other artifacts, traditions, beliefs, values, and behaviors contribute to the development and transmission of culture. RL.6.4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including those that allude to significant characters found in mythology (e.g., Herculean). RI.6.3 Explain events, procedures, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text, including what happened and why, based on specific information in the text. RI.6.7 Interpret information presented visually, orally, or quantitatively (e.g., in charts, graphs, diagrams, time lines, animations, or interactive elements on Web pages) and explain how the information contributes to an understanding of the text in which it appears. RI.6.9 Integrate information from two texts on the same topic in order to write or speak about the subject knowledgeably. W.6.6 With some guidance and support from adults, use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing as well as to interact and collaborate with others; demonstrate sufficient command of keyboarding skills to type a minimum of one page in a single sitting. Focus Questions/Big Idea/Goal (List all 3) What question(s), big idea(s), and goals drive your instruction? Focus Questions: What are some ways people have used to communicate in the past and the present? Big Ideas: Make comparisons between modern day text messaging techniques and the use of hieroglyphs as forms of communication. Goal: Students will understand the meaning and purposes of other cultures form of communication. Lesson Objective(s) Objectives are measurable. Identify certain Egyptian hieroglyphs and recognize their meanings and uses. Become familiar with aspects of ancient Egyptian culture and religion and their relationship to hieroglyphs. Analyze how hieroglyphs were used to record history, promote international relations and create power for the pharaohs. Become familiar with how to correctly read and translate simple hieroglyphs. Use a hieroglyph name generator to write their name. Revised Spring 2011 Vocabulary/ Academic Language What opportunities will you provide for students to practice content language/vocabulary and develop fluency ? Hieroglyph, tomb, temples, obelisks, papyrus, pharaoh, shen, ankh, wedjat, ideograms, and scroll Material/Resources What do you need for this lesson? Video Clips: Egypt’s Golden Empire Website, http://pbs.org/empires/egypt/index.html. Large sheet of butcher paper for each student Copies of the hieroglyphic alphabet Pencils Pens Colored markers Colored pencils Crayons Paint Copies of ideograms Scroll Glue Pictures Scissors Assessment/Evaluation Formative: How will students demonstrate understanding of lesson objective(s)? How will you monitor and/or give feedback? Student will receive participation grade for class activities. Students will present their posters to the class and the classmates will translate the hieroglyph posters. Summative: What evidence will you collect and how will it document student learning/mastery of lesson objective(s) Students will be graded on their accuracy when completing the multiple choice quiz on hieroglyphics. Instruction (Include a suggested time for each major activity) List Questions for higher order thinking These cannot be answered by yes or no. (Identify Bloom’s Level of Thinking) Level I Knowledge: What is papyrus? students’ academic, social, and cultural characteristics. Time: 6 minutes Level II Comprehension: Can To create student interest, the teacher will put several text messages on the you identify an example of a board before the students come in the room. Have the students translate form of communication in some the text messages. Put some of the hieroglyphic symbols on the board Ancient Egypt? too. Write a text messages using hieroglyphics. Have the student guess the message. Tell the students that Egyptians wrote on papyrus. Set/Motivator: How will you engage student interest in the content of the lesson? Use knowledge of Instructional Procedures/Learning Tasks: Provide specific resources/details of lesson content and delivery. Time: 40 minutes 1. Tell students about Egyptian hieroglyphs, referring to the information in the “set”. 2. Explain to students that they will be learning about Egyptian hieroglyphs and how they were used in the everyday life of the ancient Egyptians. 3. Teacher will explain why hieroglyphs are historically significant in teaching us about Egypt’s history, customs, and life in ancient Egypt. Level I Knowledge: Can the student recognize the basic components of culture (i.e., language)? Level II Comprehension: Can you distinguish how early writing forms in Egypt influenced life (i.e. religion and Revised Spring 2011 Time: 5 minutes 4. Have students view the video clips about Amenhotep’s diplomatic strategies to see pharaohs used of hieroglyphics to stay in power. 5. Hand out copies of the Egyptian alphabet to each child as well as the butcher paper. 6. Read aloud an ancient Egyptian sentence to the students. 7. Show the students how the Egyptians would have written their names. 8. Have some students come to the board and spell their name to become more familiar with the language. 9. The teacher will tell the students, they will be Egyptian scribes. Each child will write his or her name in hieroglyphs, followed by ideogram of his or her choice. 10. Remind the students to work very slowly and carefully. 11. Have the students to create a one to two sentence message using Egyptian hieroglyphs. 12. Students will write down the translation of the message on the back of the paper. 13. Post messages on the wall and have the students translate each poster. Closure: Verbalize or demonstrate learning or skill one more time. May state future learning. Time: 6 minutes The teacher will show another message and have the students to translate the message on paper. The teacher will ask what language is it. The teacher will show different forms of communication from other cultures. culture)? Level III Application: Can you apply text messages to hieroglyphics? Level IV Analysis: Can the students compare and contrast text messages and hieroglyphics? Level III Synthesis: Can you write and decipher messages using various alphabets? Level V Synthesis: How would you write your name in hieroglyphics? Level V Synthesis: How can the students rewrite a sentence from ancient Egypt to 21st century language? Level VI Evaluation: Based on the information about hieroglyphs, how would the students interpret the following language: Spanish Adaptations to Meet Individual Needs: How will you adapt the instruction to meet the needs of individual students? Include ELL?; SPED?; Gardner’s Learning Styles - Name and specify what happens in the lesson that uses each learning style listed; Other individual needs of the students/class you are teaching? ELL students will be allowed to write in their native language and posting on the wall and have the English speaking students translate their message. SPED students will use visual aids (pictures) and work with a partner to make their poster. Gardner’s Learning Styles: Artistic intelligence: Students will show their create side by forming Interpersonal intelligence: Students will work together to transcribe the messages. Linguistic intelligence: Students will show their ability to interpret another language. Intrapersonal intelligence: Students will compose their name in a different language to demonstrate understanding of another language. Logical intelligence: Students are able to see and relate 21st century text messages to hieroglyphs and explore the patterns and relationships. Management/Safety Issues: Are there any management and/or safety issues that need to be considered when teaching this lesson? Make sure students do not cut themselves with the scissors or eat the glue. Rationale/Theoretical Reasoning: The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to the writing and art of ancient Egypt through hieroglyphs. The student will learn that one of the oldest writing Revised Spring 2011 systems in the world is hieroglyphics and that each symbol represents sound. The student will develop an understanding that hieroglyphics was used as a form of communication, record keeping, and a way to preserve writing language to the gateway of the past, by the use of text message in the 21st century students will be able to see the connection of the past to the present. References: Egyptian Symbols and Figures: Hieroglyphs retrieved on 3/2/2013 from http://edsitement.neh.gov/lesson-plan/egyptian-symbols-and-figures-hieroglyphs. GreatScott! Website, http://www.greatscott.com. Retrieved on March 2, 2013. Reflections/Future Modifications: To what extent did the class learn what you intended them to learn? What will be your next steps instructionally? What did you learn about your students as learners? What have you learned about yourself as a teacher? Revised Spring 2011