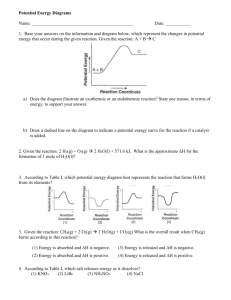
Chemical Reactions Part 2 Study guide answers
advertisement
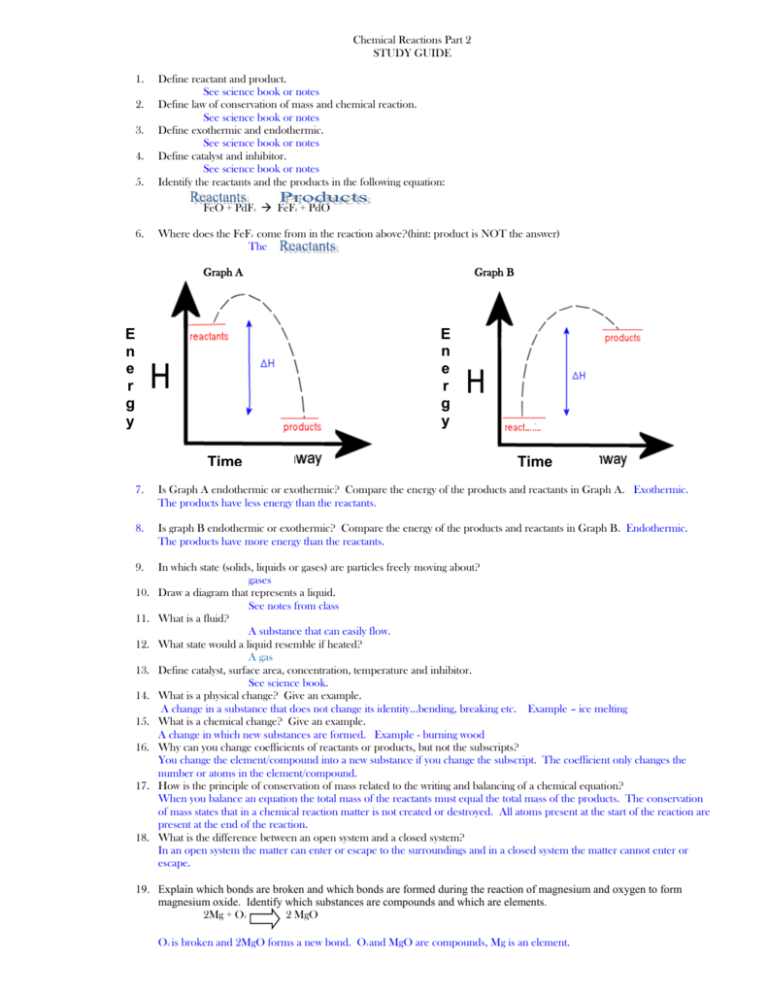
Chemical Reactions Part 2 STUDY GUIDE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define reactant and product. See science book or notes Define law of conservation of mass and chemical reaction. See science book or notes Define exothermic and endothermic. See science book or notes Define catalyst and inhibitor. See science book or notes Identify the reactants and the products in the following equation: FeO + PdF FeF + PdO 2 6. 2 Where does the FeF come from in the reaction above?(hint: product is NOT the answer) The 2 Graph A Graph B E n e r g y E n e r g y Time Time 7. Is Graph A endothermic or exothermic? Compare the energy of the products and reactants in Graph A. Exothermic. The products have less energy than the reactants. 8. Is graph B endothermic or exothermic? Compare the energy of the products and reactants in Graph B. Endothermic. The products have more energy than the reactants. 9. In which state (solids, liquids or gases) are particles freely moving about? gases Draw a diagram that represents a liquid. See notes from class What is a fluid? A substance that can easily flow. What state would a liquid resemble if heated? A gas Define catalyst, surface area, concentration, temperature and inhibitor. See science book. What is a physical change? Give an example. A change in a substance that does not change its identity…bending, breaking etc. Example – ice melting What is a chemical change? Give an example. A change in which new substances are formed. Example - burning wood Why can you change coefficients of reactants or products, but not the subscripts? You change the element/compound into a new substance if you change the subscript. The coefficient only changes the number or atoms in the element/compound. How is the principle of conservation of mass related to the writing and balancing of a chemical equation? When you balance an equation the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. The conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction matter is not created or destroyed. All atoms present at the start of the reaction are present at the end of the reaction. What is the difference between an open system and a closed system? In an open system the matter can enter or escape to the surroundings and in a closed system the matter cannot enter or escape. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Explain which bonds are broken and which bonds are formed during the reaction of magnesium and oxygen to form magnesium oxide. Identify which substances are compounds and which are elements. 2Mg + O 2 MgO 2 O is broken and 2MgO forms a new bond. O and MgO are compounds, Mg is an element. 2 2