Chapter 17 - Reading Guide- Classification Name Period Date Part

Chapter 17 - Reading Guide- Classification Name
Period Date
Part A- Vocabulary: These are SOME of the vocab words for this unit, you are not required to write each
definition, but you will need to know them for the test!!
Biodiversity
Taxonomy
Taxon
Kingdom
Domain
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Binomial nomenclature
Systematics
Phylogenetics
phylogenetic diagram
cladistics
shared character
derived character
clade
cladogram
bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Eubacteria
Archaebacteria
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
Part B- Reading Guide: Answer the following questions as you read through the chapter. The questions are in order, but be sure to read any information in the margins. Be thorough in your answers. Try to answer in your own words (it will help you learn more!). Questions with the word THINK are not directly said in the book, you actually have to think about them!!
1.
Over time, scientists have created various systems of classification to
. Each system places species into categories
2.
3.
What is biodiversity?
How many insect species did Terry Erwin estimate there could be on Earth?
4.
Do you THINK it’s a good idea to classify organisms into groups based only on their physical appearance? Why or why not?
5.
The science of describing, naming, and classifying organisms is called
6.
What is a taxon?
7.
Why do you THINK Aristotle’s classification system was inadequate?
8.
What is a drawback of using common names?
9.
List Linnaeus’ Levels of Classification from largest to smallest (start with Domain even though it was not used by Linnaeus.
10.
You will need to memorize the levels of classification for this unit’s test, so come up with an acronym to remember it (you may use one you already know). An acronym is where you take the first letter of which word and create an easy to remember phrase. An example would be “Dumb Kings Play Chess On
Fine Grain Sand.” Now create your own
11.
What is the name of the naming system used by Linnaeus?
12.
What are the two parts of this system?
13.
Why are scientific names better than common names? (THINK)
14.
What is a subspecies?
15.
Modern biologists consider not only visible similarities but also similarities in
16.
What is the goal of systematics?
17.
What is phylogeny?
18.
What is phylogenetics?
19.
What types of evidence to systematists us to hypothesize about phylogenetics?
20.
Systematists often represent their hypotheses in the form of a
21.
called a .
What kinds of organisms are missing from the fossil record?
22.
The greater the number of homologous features shared by two organisms, the
23.
What feature do all amniotes have in common?
24.
What 3 types of organisms are amniotes?
25.
What is cladistics?
26.
What is the difference between a shared character and a derived character?
27.
What term is used to describe an ancestor and all of its descendents in cladistics?
28.
Phylogenetic diagrams in cladistics are called
29.
What is an out-group?
.
, also
30.
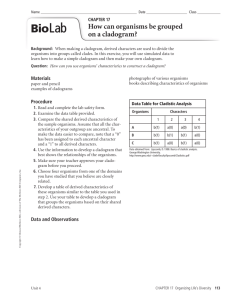
Fill in Table 17-2 and draw Figure 17-4 next to it. Read the “Constructing a Cladogram” section and summarize how the table is related to the figure.
Table 17-2- Data Table for Cladogram
Characters
Group of
Organisms
Mosses
(outgroup)
Ferns
Vascular
Tissue
Seeds Flowers
Pine Trees and other conifers
Flowering plants
31.
On a molecular cladogram, branch lengths are
32.
How are macromolecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins molecular clocks?
35.
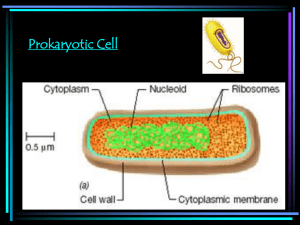
What is the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
36.
Carl Woese proposed how many kingdoms?
37.
What organelle does ALL life have?
38.
Why are rRNA genes useful for studying basic evolutionary relationships?
33.
What do similar banding patterns on chromosomes between two different species tell scientists?
34.
Systematists will use data about physical features,
39.
40.
What is the last universal form of life?
What are the three major lineages, or domains?
41.
What are the characteristics of the domain Bacteria?
42.
What are the characteristics of the domain Archaea?
43.
What are the characteristics of the domain Eukarya?
44.
Fill in the Data Table below using Figure 17-3.
Taxon
Domain
Bacteria
(kingdom
Eubacteria)
Domain
Arachea
(kingdom archaebacteria)
Domain
Eukarya-
Kingdom
Protista
Domain
Eukarya-
Kingdom Fungi
Domain
Eukarya-
Kingdom
Plantae
Domain
Eukarya-
Kingdom
Animalia
Cell Type
Kingdom and Domain Characteristics
Cell Surfaces Body Plan Nutrition
45.
Do taxonomic systems change as we discover more about the relationships between organisms?