Biological Classification System Assignment
advertisement

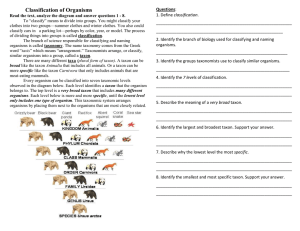
Biological Classification System Assignment NAME: PERIOD: Objective Answer the following questions 1-10 on your own paper, using full sentences where appropriate. Use your text book chapter 17 pg 518>. Questions 11 and 12 fill in the tables on this paper. 1. Vocabulary: Write definitions for the following words using Chapter 17 and the glossary: taxonomy, taxon (taxa) binomial nomenclature, phylogeny, cladistics, cladogram, derived characters. 2. Give one reason why organisms are classified into a hierarchical classification system by scientists 3. Give an example of a group of things you classify in your life, how do you decide to group them. (what’s the criteria?) 4. Who was Linnaeus? 5. Write down the common name then the scientific name for any species. I identify which part of the name is the genus and which is the species. Which of these is the broadest taxon? 6. Write down the seven levels (taxon) in the classification system in the correct order from broadest to most specific. Look at Fig 17.3 on pg 520, why do organisms keep getting eliminated as you look down the taxon levels? 7. Provide the full scientific classification for either the West Indian Manatee or the American Alligator (Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species) 8. State how scientists classify organisms- How do they decide one organism belongs in the same group as another organism, or that another organism belongs in a different group. (hint pg 524>) 9. Complete the quick lab pg 525 Construct a Cladogram. 10. Over time how we classify organisms has changed. How has the classification system changed over time? (hint pg 521, 524, 533) 11. Domains: Complete the Chart using pg 534 and pg 535 Domain Name Characteristics Kingdoms included 12. Complete the 6 Kingdom chart: Gather the required information to describe the main characteristics of each of the six kingdoms. (hint old biology text book pg 459) Classification of the Six Kingdoms Domain Archaea Bacteria Eukarya Eukarya Eukarya Eukarya Kingdom Archaebacteria Bacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Cell type (prokaryotic/ eukaryotic) Number of cells (uni or multicellular) Significant cell structures Nutrition (autotrophic/ heterotrophic etc..) Reproduction (sexual, asexual, binary fission) Movement (yes or no) One specific example