39 Cladistics
advertisement

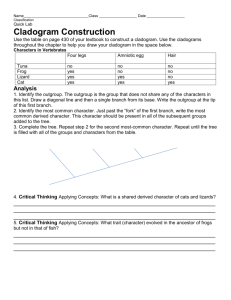
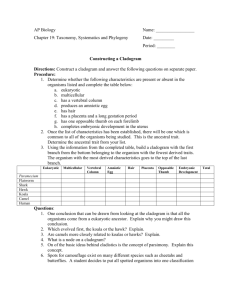
HL IB-Biology 2011/12 #39 CLADISTICS D.5 Phylogeny and Systematics Assessment Statements Addressed: D.5.5 Define clade and cladistics. D.5.7 Outline the methods used to construct cladograms and the conclusions that can be drawn from them. D.5.8 Construct a simple cladogram. D.5.9 Analyze cladograms in terms of phylogenetic relationships. D.5.10 Discuss the relationship between cladograms and the classification of living organisms. ➡ To learn about cladistics and how to construct a cladogram go to the following websites: http://www.brooklyn.cuny.edu/bc/ahp/CLAS/CLAS.HP.html, click on cladistics and read the information. Later you might want to explore the other chapters. http://ccl.northwestern.edu/simevolution/obonu/cladograms/Open-This-File.swf. This is a cute movie about how to make cladogram. As of June 16, 2009, the site was still in process of being developed. http://www.eeescience.utoledo.edu/Faculty/Dwyer/Biodiversity/ConstructingCladograms.htm, 1. Study the steps on how to construct a cladogram, then apply the same steps to construct your own cladogram with the following organisms and characteristics: Organisms: Paramecium, flatworm, shark, hawk, koala, camel, human Characteristics: eukaryotic, multicellular, has a vertebral column, produces an amniote egg, has hair, has a placenta, has one opposable thumb on each forelimp 2. For analyzing some cladograms go to http://hlbiology.wordpress.com. Under ‘Topic Pages’ find ‘Option D’ and download the powerpoint titled ‘Tree Thinking Challenge. Each slide of the powerpoint has a question. Determine the answer first BEFORE revealing the answer by clicking on any key on the keyboard (advancing the PowerPoint presentation)! Labudda, CHS, 39 Cladistics.pages ‘PAPER-PENCIL’ ACTIVITY: FROM RESTRICTION MAP TO CLADOGRAM Adapted from http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/WWC/1995/simulation_restriction.php, Background Cladistics is a system of classification, which group taxa together according to the characteristics which have most recently evolved by comparing how many primitive and derived characteristics organisms share. You will compare the restriction map of DNA of six different primate species and use the number of differences to show which species are more closely related (share a more recent common ancestor). You will show the number of shared characteristics using a cladogram Restriction Maps: A particular restriction nuclease will cut DNA into a series of fragments called restriction fragments. If you treat DNA with a number of restriction nucleases, you can construct a map that shows the location of each of these cuts on a given length of DNA. In the example below, Species 2 has three differences with Species 1. The positions of the differences are indicated by the ‘X’. Instructions Below are restriction maps for a segment of a gene, which codes for hemoglobin, common to a number of mammals including humans. 1. Compare the restriction map for each species to the human map. Make a mark on the map for each difference. A difference is the addition or subtraction of a restriction site. (See the example). 2. For each restriction map, count the number of differences that you find. 3. Construct a cladogram based on the data. Data: Restriction Map of Human and Various Primate DNA in a Cluster of Genes Coding for Hemoglobin Data Table and cladogram: 1. Discuss the cladogram. 2. Discuss the relationship between cladograms and the classification of living organisms.