PA study guide plant diversity and evolution (I) 2012
advertisement

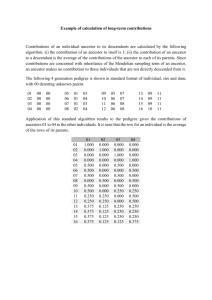
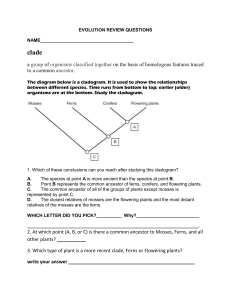
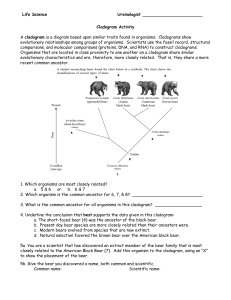
Plant and Animal Biology – Study Guide Plant diversity and evolution (I) I) Name:______________________Date:_______Period:__ General principles of biological classification (chapter 16) List the seven levels of classification in order from general to specific: How are problems addressed when a group seems to fit “between” categories? Compare and contrast taxonomy and systematics Describe the science of cladistics. What is a cladogram? Explain what is meant by a primitive character state and a derived character state: Species A and B are more closely related to each other than either is to C, D, E, or F. Species C and D share a common ancestor not shared by the other 4. E and F also share a common ancestor not shared by the other 4. C, D, E, and F share a common ancestor separate from A and B. Draw a cladogram for these 6 species: II) General features of the plant kingdom (chapter 20): Major pigments: Food storage product: Cell wall material: The ______ ______ forms during cell division. The above are shared by _______ _______, indicating common ancestry with the plant kingdom. Plants also have the following derived characteristics (adaptations to life on land): Fatty (wax) cuticle: Stomata: Multicellular, dependent embryos: III) Plant life cycle: Alternation of generations (p. 227-8): this is important; so to be sure you get it draw a cycle diagram with labels AND describe the process in words: