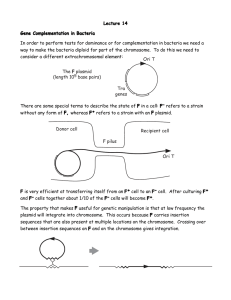
Prokaryote Genetic Exchange
advertisement

Genetic Variability in Bacteria Mutation spontaneous vs inducible point mutations silent, missense, nonsense, frameshift forward vs reverse (reversion & suppression) macrolesions Genetic Exchange Transformation Conjugation Transduction Transposable elements Genetic Exchange • Recombination: – Reciprocal: 2 x dsDNA with common sequence regions swap (cross-over) – Nonreciprocal: ssDNA forms heteroduplex with dsDNA – Site-specific – Transposition • • • • Transformation Conjugation Transduction Transposons See Holliday Model (Fig. 13.2 ) Griffith’s Transformation (1928) Avery, MacLoed & McCarty (1944) concluded DNA! Transformation • DNA fragments from environment get recombined into the chromosome. • Natural mechanisms of DNA uptake vary among bacteria. • Artificially facilitated by chemically treating cells (competent cells), or by electrical pulse. Conjugation (“Bacterial Sex”) • • • • • F+ cell is donor. F- cell is recipient. F+ x F- mating. Bound by F+ cell pilus Transfer by rolling circle mechanism. F-Plasmid Replication for Transfer • “Rolling Circle Mechanism” – – – – Relaxosome nicks DNA Extend at 3’-OH. Displace parent strand. Synthesize complement for displaced strand. • Viral Replication – Same mechanism – Multiple copies made from a single initiation. F-factor Integration • F-factor recombines (single crossover) with F+ cell chromosome at an insertion sequence (IS). • High frequency of recombination Hfr cell created. • Precise de-integration reverses Hfr back to F+. • Imprecise de-integration converts Hfr to F’. IS IS Facilitated Plasmid Integration What is an F’? Hfr F’ Chromosomal Gene Exchange • Hfr or F’ cells may result in transfer and recombination of chromosomal genes to F- cell. • F’ factor has chromosomal DNA; transfers like a normal F factor to the recipient, making a new F’. • Hfr can initiate transfer via the rolling circle mechanism; typically transfer of the chromosome is incomplete; only a fragment gets incorporated. • Viruses of bacteria are called a phage. • Phage protein coat surrounding DNA is called a capsid. • During phage replication and assembly, capsids may package chromosomal or plasmid DNA by mistake. • When transferred to a new host it may recombine. Transduction Transducing particle Transposable Elements: “Jumping Genes” • Transposable elements (insertion sequences and transposons) can tranfer copies of themselves within or to other DNA molecules (chromosome, pDNA, or vDNA). • Antibiotic resistance genes rapidly spread within and between bacterial populations by composite transposons carried on F factors called R plasmids. Self-replicative recombination •Transposon or IS self-replicates copy to splice into DNA at a specific target sequences. • Endonuclease activity cuts target sequence, leaving single strand overhanging ends. •Transposon is ligated to ends. • Gaps are filled by DNA polymerase to yield a target sequence at each side of the transposon (called direct repeats). • Specific details of the process are more involved (Fig 13.10). Effects of Transposon Activity • Insert to mutate genes; change phenotype. • Influence transcription or translation (on/off) – Promoters activate – Stop codons and terminator sequences inactivate – Useful tool in gene purification and function studies • Facilitate plasmid fusion. • Conjugative transposons with transfer genes. • Transfer antibiotic resistance. – Plasmid to plasmid – Plasmid to chromosome Consequences of Genetic Exchanges • Facilitate macrolesions; mutations of large sequence regions of DNA: – deleted – inserted – Inverted – duplicated. abcdefg → abcdefg → abcdefg → abcdefg → • Spread beneficial trait: – Intraspecific – Interspecific • Antimicrobial resistance abfg abcxyzefg abedcfg abcdecdefg