Genetics Test Study Sheet
advertisement

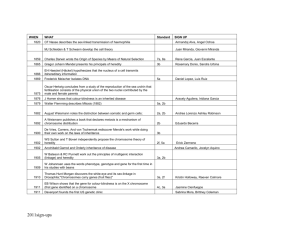
Genetics Test Study Sheet Where Heredity Goes Wrong Mutation -A sudden change in the gene or chromosome Types of Mutation 1. Gene mutations -Point mutation -Mutation of single gene on a chromosome -Involves one or two nucleotides -Generally occur during replication Ex/ Cystic fibrosis, sickle cell, Huntington’s a) Substitution -An incorrect nucleotide is substituted in place of the correct one -Only one protein affected CTGGAG CTGGGG b) Insertion -One base is inserted from the sequence CTGG AG CTGG TGG AG c) Deletion -One base is deleted from the sequence CTGGAG CTAG Insertions and deletions can be really harmful since adding or deleting a nucleotide shifts the whole reading of the codons. It is also known as frame shift mutations. 2. Chromosome mutations -Involves changes in number or structure of chromosomes -Usually a failure in separation during meiosis a) Deletion -Loss of all or part of the chromosome b) Duplication -Extra copy of all or part of chromosome c) Inversion -Reverses parts of a chromosome d) Translocation -When part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another e) Nondisjunction -Failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis Bacterial Transformation Biotechnology -Application of technological process to living organisms 1) Production of medicine 2) Gene therapy/ treating diseases 3) Insect/ herbicide resistant crops -Use gel electrophoresis to find certain genes Transformation -When one bacteria is changed by the gene from another strain of bacteria Recombinant DNA -DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources -Makes it possible to change the genetic composition of an organism Plasmids -Separate circular DNA found in bacteria -Widely used in recombinant DNA 1) Use restriction enzymes to cut the DNA and the plasmid so both have “sticky ends”. 2) Insert DNA into the plasmid. 3) Then, re-insert the plasmid into a bacterial cell which can rapidly divide Studying the Human Genome Restriction Enzymes -Produced by bacteria -Used to cut DNA molecules into restriction fragments -Each enzyme cuts a specific DNA Gel Electrophoresis -Separates and analyzes restriction fragments which is stained -Run DNA through a gel using electric current -DNA (Neg. charged) will move to the opposite end of the gel (Pos. charged) -Smaller fragments will move faster and farther -Bands of varying lengths are visible Human Genome Project -International effort to sequence all 3 billion base pairs of human DNA and identify all the genes. -Pinpointed genes of many diseases and disorders -Identified 3 million locations where single-base DNA differences occur in humans What’s the Point? 1) Can lead to better, less expensive and more nutritious food. a) GM food -Produce higher yield of crops -Are modified to be resistant to bugs and herbicides -Growth hormones injected into certain animals -Hoping to clone animals to increase food supply and save endangered species 2) Human health can be improved a) Preventing disease b) Medical research c) Treating disease Ex/ Gene therapy -Process of changing a gene to treat medical disorder -Replacing faulty gene with normal one d) Diagnosing disease Ex/ Genetic testing Selective Breeding -Allowing animals with wanted characteristics to breed Inbreeding -Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics -Offspring has an increased chance of genetic defect Hybridization -Crossing different individuals to bring together the best of both organisms -Offspring usually stronger than the parents Finding Something Wrong Karyotype: -Way to organize a set of chromosomes. -Used to see if there’s anything abnormal. *Know how to determine if a person has a genetic disorder or not*