Semester 2 Final Review
advertisement
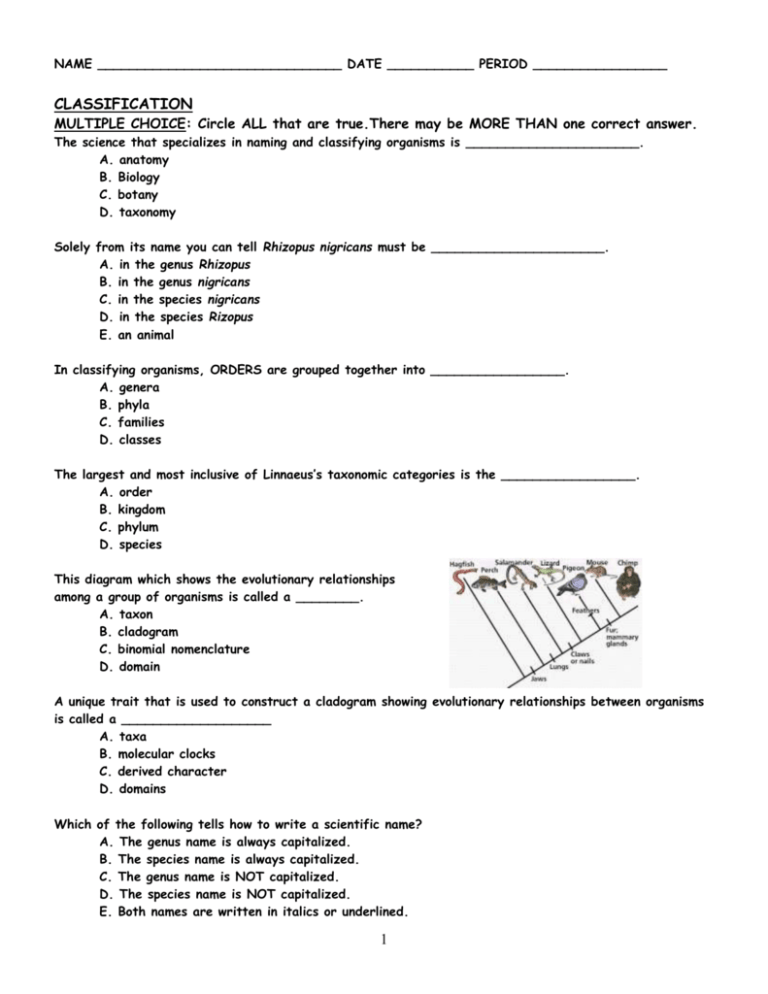
NAME _______________________________ DATE ___________ PERIOD _________________ CLASSIFICATION MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle ALL that are true.There may be MORE THAN one correct answer. The science that specializes in naming and classifying organisms is ______________________. A. anatomy B. Biology C. botany D. taxonomy Solely from its name you can tell Rhizopus nigricans must be ______________________. A. in the genus Rhizopus B. in the genus nigricans C. in the species nigricans D. in the species Rizopus E. an animal In classifying organisms, ORDERS are grouped together into _________________. A. genera B. phyla C. families D. classes The largest and most inclusive of Linnaeus’s taxonomic categories is the _________________. A. order B. kingdom C. phylum D. species This diagram which shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms is called a ________. A. taxon B. cladogram C. binomial nomenclature D. domain A unique trait that is used to construct a cladogram showing evolutionary relationships between organisms is called a ___________________ A. taxa B. molecular clocks C. derived character D. domains Which of the following tells how to write a scientific name? A. The genus name is always capitalized. B. The species name is always capitalized. C. The genus name is NOT capitalized. D. The species name is NOT capitalized. E. Both names are written in italics or underlined. 1 TRUE – FALSE Change the underlined word or phrase to make the statement correct. __________ __________ __________ __________ The least inclusive group to which an organism can belong is the kingdom. Bird wings and insect wings are homologous structures. Most organisms in the kingdoms Animalia and Plantae are multicellular. A species is a larger taxonomic unit than a genus. NAME THE THREE DOMAINS in the THREE-DOMAIN SYSTEM: _________________________ __________________________ __________________________ MATCHING: Match the description of organisms with its KINGDOM: ______ Eukaryotic heterotrophs whose cell walls contain chitin ______ Prokaryotes whose cell walls contain peptidoglycan ______ Multicellular autotrophs with chloroplasts whose cell walls contain cellulose A. B. C. D. E. F. EUBACTERIA ARCHAEBACTERIA PROTISTA PLANTAE FUNGI ANIMALIA ______ Prokaryotes whose cell walls lack peptidoglycan ______ Heterotrophic multicellular eukaryotes without cell walls or chloroplasts ______ Unicellular, colonial, or multicellular eukaryotes that show the widest variety of characteristics Refer to the illustration above, This type of diagram is called a ___________________________ Which of the organisms in the above diagram have lungs? 2 EVOLUTION STARTS WITH? 1. E __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __, or change over time, is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms 2. A scientific T __ __ __ __ __ is a well supported, testable explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world. 3. C __ __ __ __ __ __ D __ __ __ __ __ was an English naturalist who made numerous observations during his travels on the Beagle which led him to pose a hypothesis about how life changes over time. 4. F __ __ __ __ __ __ are the preserved remains of ancient organisms that provide evidence for how life has changed over time. 5. L __ __ __ __ __ __ proposed that the selective use or disuse of an organ led to a change the organ that was then passed on to the offspring. 6. F __ __ __ __ __ __ is the ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in its specific environment. 7. Any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival, like webbed feet, sharp claws, or speed, is called an _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 8. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ T __ __ F __ __ __ __ __ __ 9. Structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues are called H __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 10. Homologous structures that are so reduced in size that they no longer function, like the human appendix or legs in skinks, are called _V_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ organs 11. Choosing to breed cows that produce the most milk or the fastest horses is termed A __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 12. Charles Darwin’s observations of finches and turtles on the G __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ Islands led to his Theory of E __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. Dolphins, penguins, and sharks are distantly-related species that share similar characteristics which help them live in water. This is an example of C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ evolution. 14. Even though the Galapagos finches share a common ancestor, they have evolved to fit the ecosystems of their individual islands. This is an example of D __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ evolution. 15. Traits that are learned and not inherited are called A __ __ __ __ __ __ T __ __ __ __ __. Which of the following best describes how LAMARCK would explain giraffes with long necks? A. Long-necked giraffes eat more grass than short necked giraffes so their necks grow longer. B. Natural variation in the population produces some longer and some shorter-necked giraffes and longer necked giraffes can reach food more easily. C. Some giraffes have acquired longer necks by stretching to reach food and passed that trait on. D. Giraffes just started out with long necks and haven’t changed. On the Galapagos Islands, Darwin discovered birds with differently shaped beaks. What might this tell you about the eating habits of the birds on different islands? Explain your answer. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the letter of the ONE BEST answer that completes the statement. Structures that have different mature forms, but develop from the same embryonic structure are called _______________ structures. A. Darwinian B. Lamarckian C. homologous D. fossils Because of its similarities to artificial selection, Darwin referred to the “survival of the fittest” as __________________________, A. use it or lose it B. natural selection C. homologous structures D. struggle for existence The natural differences between individuals of a species are referred to as________________________ A. fitness B. natural selection C. adaptations D. variations When farmers select the largest hogs, the fastest horses, or the cows that produce the most milk for breeding it is called ________________. A. natural selection B. artificial selection C. survival of the fittest D. homologous variation An inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce in its specific environment is called a(n) __________________. A. homologous structure B. vestigial organ C. adaptation D. speciation The bones in the diagram at the left are examples of ____________ A. homologous structures B. embryonic mates C. vestigial organs All of the A. B. C. D. following play a role in Darwin’s Theory of Evolution EXCEPT __________________________ natural variation survival of the fittest struggle for existence inheritance of acquired traits 4 5 6