Classification The arrangement of organisms into orderly groups
advertisement

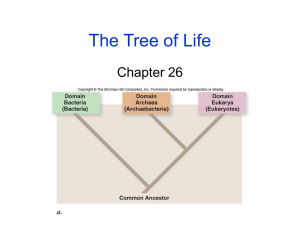
Classification The arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities The branch of biology that involves classifying is called taxonomy Taxonomists are scientists that identify & name organisms Benefits of Classifying Accurately & uniformly names organisms Uses same language, Latin or some Greek, for all names Basis for Classification Structural similarities, likely evolved from common ancestor Ex: lynxes and bobcats If number & structure of chromosomes are similar, may have common ancestor Ex: cabbage, cauliflower and kale -> almost identical chromosome structure Similar organisms have similar DNA sequence Ex: giant panda is more closely related to a bear than the red panda Classification Groups Taxon (taxa-plural) is a category into which related organisms are placed There is a hierarchy of groups (taxa) from broadest to most specific Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Dapper King Phillip Came Over From Germany Singing) Domains Broadest & most inclusive taxon 3 domains Archae & Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane bound-organelles) Eukarya are more complex (have a nucleus & are membrane-bound organelles) Archaea 1st cells to evolve live in harsh environments found in sewage treatment plants, thermal or volcanic vents, hot springs or geysers that are acid or very salty H2O such as the Dead Sea or the Great Salt Lake Eubacteria some cause disease found in ALL habitats EXCEPT harsh ones important decomposers for the environment commercially important in making yogurt, cottage cheese, and buttermilk Domain Eukarya is divided into Kingdoms Protista – Ex: paramecium, slime mold o Most are unicellular, some multicellular o Some are autotrophic, while others are heterotrophic o Aquatic Fungi - Ex: mushrooms, yeasts o Multicellular, except yeast o Absorptive heterotrophs (digest food outside their body & then absorb it) o Cell walls made of chitin Plantae (multicellular plants) – Ex: mosses, ferns o Autotrophic o Absorb sunlight to make glucose – photosynthesis o Cell walls made of cellulose Animalia (multicellular animals) Ex: fish, reptiles o Ingestive heterotrophs (consume food & digest it inside their bodies) o Feed on plants or animals Taxons Most genera contain a number of similar species The species homo is an exception (only contains modern humans) Classification is based on evolutionary relationships Cladogram – diagram showing how organisms are related based on shared, derived, characteristics such as feathers, hair, or scales Dichotomous Keying Used to identify organisms Characteristics given in pairs Read both characteristics and either go to another set of characteristics OR identify the organism Early Taxonomists Aristotle was the 1st taxonomist He divided organisms into plants and animals Further subdivided them by their habitat – land, air, or sea dwellers Linnaeus classified organisms by their similar structure Developed naming system still used today, uses Latin Called “the Father of Taxonomy” Developed the modern system of naming known as binomial nomenclature, genus & species Standardized Naming System Italicized in print Capitalize genus, but NOT species Underline when writing Convergent Evolution – different organisms that live in similar environments become more alike in appearance & behavior Ex: bird wings/insect wings Coevolution – when 2 species evolve together. There is a mutual evolutionary influence between 2 species. The species have a symbiotic relationship. Ex: birds & flowers Divergent evolution – ancestral species gives rise to a number of new species that are adapted to different environmental conditions and are less alike. Ex: Darwin’s finches Punctuated Equilibrium – some populations don’t change much over time, but have rapid periods of change in between long stable periods Ex: horseshoe crab haven’t evolved much but fossil records show short periods of speciation.





![[Type text] Taxonomy and Classification Notes Taxonomy: the study](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006833839_1-e22256a74f9158844d75d24ddb12e551-300x300.png)