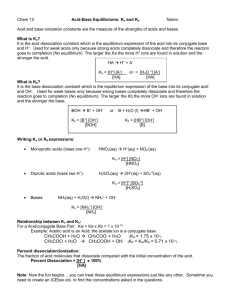
Summary of Formulas
advertisement

SCH 4U Acids and Bases Worksheet! Name _______________________ pg 488 – 509 Summarized A few different people throughout history have had ideas about the nature of acids and bases. Svante Arrhenius said that Acids produce _________ in aqueous solution. Another name for the hydrogen ion is the ___________. He also said that bases produce _____________ in aqueous solution. This idea became known as the Arrhenius theory. According to Arrhenius what would the following become in aqueous solution H2SO4 Ca(OH)2 Johannes Bronsted and Thomas Lowry came up with an idea as well regarding acids and bases. They said that an Acid was a proton (hydrogen ion ) _____________________ and a base was a proton (hydrogen ion) _____________________. What happened to the H+ when it entered solution? __________________________________________ This became known as the Bronsted-Lowry theory According to Bronsted and Lowry, how would the following interact in water? HCl + H2O NH3 + H2O This made more sense because it could be reversed and would allow equilibrium to establish. Because of this forward and backwards reaction there needed to be the possibility for transfer in both directions. This meant there had to be a Bronsted Lowry acid and base on both sides of the chemical equation. This led to the idea of ______________________________________ pairs. How is the conjugate acid formed? ___________________________________________________ How is the conjugate base formed? ___________________________________________________ Write the general equation for how an acid acts in water ______________________________________________ Write the general equation for how a base acts in water ______________________________________________ Indicate the conjugate acid base pairs in the following equations HF + H2O _____________ _______________ NH3 + F- = H2O ____________ NH4+ = _____________ _______________ + ____________ H3O+ __________________ + OH__________________ Notice that conjugate acids and base differ from each other by only 1 Hydrogen ion (proton) each time! This is how you determine the pairings. If you know the identity of any one substance (eg/ base) you can determine the identity of all other substances in the equation. Some substances can be acids or bases depending on the reaction. These are called _________________ substances. Draw how hydrogen Carbonate (HCO3-) can act as both an acid and a base in different situations HCO3- (acid) + H2O (base) HCO3- (base) + H2O (acid) The Acid ionization Constant! The Acid ionization constant ( Ka ) is the constant that relates to acids when they reach equilibrium. It has the same equation used for other equilibrium constants. Write the Acid ionization constant equation based on your general formula from the last page Ka = _________________________ What can be left out of this formula and why? The simplified Acid ionization constant equation Write the acid ionization constant equation for the equilibrium reaction of HSO4- and water Remember! In every acid-base equilibrium reaction there are always 2 acids and 2 bases. These two bases are going to ____________________ for the protons. If H2O is a stronger base than A- equilibrium position will be to the ______________ and favour ____________ If A- is a stronger base than H2O then equilibrium position will be to the ____________ and favour ____________ Complete Questions on pg 494 # 1-4, 6-8 Strong and Weak Acids As we know, acids will dissociate in water to an H+ or H3O+ and an A- ion. With a __________ acid almost all of the HA breaks down into ions With a __________ acid only some of the HA breaks down into ions and the rest remains as HA in solution. Because strong acids nearly fully dissociate, they have very large Ka values because nearly no reactants remain and only products are left. This means the equilibrium position is way to the right. Because of this [H+] almost equal to initial [HA]. With weak acids, they do not dissociate fully and have much smaller Ka values. Depending on the % of dissociation we can determine the amount of reactants and products. For these the equilibrium position is to the left and favours remaining as HA What is the connection between the strength of an acid and the strength of its’ conjugate base? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Most familiar acids are _______________ which means the hydrogen atom is attached to oxygen atoms that are usually a part of a polyatomic ion. Most organic acids are _________ acids Strong and Weak Bases Similar to acids, bases can be strong or weak depending on how much they dissociate. A _____________ base will dissociate almost ________% This means that a 1Mol solution of BOH will lead to 1 mol B+ and 1 mol OHExamples of these types of bases include NaOH and KOH and all ____________ Hydroxides. A _____________ base will not dissociate fully and often do not contain OH- in them but will react partially to create them using the formula below. One example is ____________________ B + H2O HB+ + OH- Write the equation for the base ionization constant ( Kb ) which is the constant that relates to bases when they reach equilibrium. Kb = _____________________________________ The simplified version is What is an organic base? _______________________________________________________________ Water as an Acid and a base Water can behave like both an acid and a base because of its ability to react with itself which is called the _____________________________________. The reaction for this is 2H2O H3O+ + OH- This produces an ion-product constant for water (Kw ) that is the following equation Kw = [H3O+ ] [ OH- ] [H2O]2 This can be simplified to Kw = [H3O+ ] [ OH- ] What is the [H3O+] of water? ________________________ What is the [ OH- ] of water? ________________________ What is the value for Kw then? _______________________ What is the relationship between Ka , Kb, and Kw ? Explain how they got the formula Ka x Kb = Kw Because of this trend we know… - A strong acid will have a very weak conjugate base - A strong base will have a very weak conjugate acid - A weak acid will have a weak conjugate base - A weak base will have a weak conjugate acid. Because of this, if you know Ka you can also determine Kb and vice versa for conjugate base pairs. pH and pOH What is pH? ____________________________________________ What equation is used for pH? ________________________________ What is pOH? ____________________________________________ What equation is used for pOH? ________________________________ pH + pOH always equals ____ because that is equal to the –log(Kw) Thus if you know pH , you also know pOH! How do we get the H+ concentration from a known pH? What formula do we use? _______________ How do we get the OH- concentration from a known pOH? what formula do we use? _____________ Could we figure out the OH- concentration from a known pH? Why or why not? Notice that the value of 10-x will always have a pH very similar to x. Try it for yourself! Complete Questions on Pg 509 # 1-9 Summary of Formulas pH = -log[H+] [H+] = 10-pH pOH = -log[OH-] [OH-] = 10-pOH pH + pOH = 14 Ka x Kb = Kw Kw = [H3O+ ] [ OH- ]