Acids and Bases Notes
advertisement

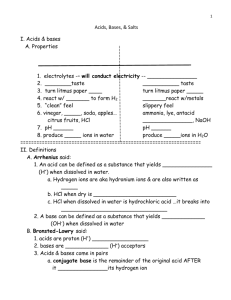
Acids and Bases Notes Electrolytes Substances that, when __________ in water, produce aqueous solutions that will __________ electricity Strong electrolytes ______________ ___________ _____________ Many _____________ compounds Weak electrolytes ________________ _____________ ______________ Solutions _________________ mixtures in which one substance is _______________ into another the “_______________” dissolves in the “_______________” example: Kool-Aid -water is the solvent, the drink mix is the solute Molarity Molarity of a solution is equal to the number of ____________ ____ __________ divided by the number of ___________ _____ _________________ New symbol [square brackets] [H+] = _______________ of H+ ions The larger the molarity, the more _________________ the solution Concentrated In a concentrated solution, the amount of solute is __________ compared to the amount of solvent it is ____________ ______ Dilute In a dilute solution, there is much more _______________ than ______________ Solutions are “____________” by adding more solvent ______________ is more dilute than ________________ Acids and bases, as we use them in the lab, are usually ______________ ___________ Ex: when we talk about “hydrochloric acid”, it is actually hydrogen chloride gas ____________ in water Concentrated acids have ______________ ______________ Ex: “conc.” HCl = 12M; H2SO4= 18M In the lab, we usually use ______________ ______________ Ex: 1.0M HCl, or 0.1M H2SO4 What is an acid? Many definitions are used ______________ ______________: a substance that produces ______________ in water Then, H3O+= ______________ ion Properties of acids React with most metals to produce _______ react with carbonates to produce ________ taste _________ damage living ______________ ______________ bases Common acids Acid formulas –start with H H3PO4 HCl HC2H3O2 H2SO4 Also written CH3COOH HNO3 What is a base? Commonly called “______________” ______________ base: a substance that produces ______________ ions when added to water Common bases There are three common varieties of bases: 1) ______________ compounds (OH-) ex: NaOH, Ba(OH)2 2) ______________ (CO32-) and ______________ (HCO3-) ex: Na2CO3, NaHCO3, CaCO3 3) ______________ (NH3) and ______________ Properties of bases React with fats and oils to produce ______ damage living ______________ feel ___________ _____________ bitter ______________ acids Hydroxide bases Release ______________ ______________ directly into the water Carbonates and bicarbonates React with water to produce ______________ ions Ammonia and amines React with water to produce ______________ ions Chemical indicators: chemicals that change colors when in an acid or base solution Phenolphthalein acids = ______________ bases = ______________ Litmus acids = ______________ bases = ______________ pH scale Used to indicate the ______________ or “______________” of a solution tells how strongly acidic a solution is…______________ how strong an acid is! Think pH as “______________” the lower the pH, the more _______, the _______ ______________ the solution The pH is the measurement of how many H+’s are in the water…NOT a measure of if the H+’s came from a “strong” or “weak” acid!!! pH scale 0-2 4 –6.99 10 -12 2 -4 7 12 -14 7.01 -10 pH calculations pOH calculations The Big Five: pH and pOH relationship In pure water at 25°C: pH = -log [H+] [H+] = [H+] = 10-pH [OH-] = pOH = -log [OH-] Therefore, And , [OH-] = 10-pOH pH + pOH = 14 Autoionization of water Water molecules can react with each other H2O + H2O H3O+ + OH At 25ºC, [H2O] is a constant Kw= [H3O+] [OH-] = 1x10-14 Let’s use [H+] instead of [H3O+] Pure water is neutral [H+] =[OH-] = 1x10-7M If ,the solution is acidic If ,the solution is basic Arrehnius neutralization Works for the reaction of a ______________ acid with a ______________ base Remember –acid (or base strength) has to do with how much of the acid (or base) ______________ in water, not directly how many______________ _____are produced What is an acid? Many definitions are used Arrhenius acid: a substance that ______________ ______________ in water Then, H2O + H+ H3O+ H3O+ = hydronium ion What is a base? Commonly called “______________” Arrhenius base: a substance that ______________ ______________ ions when added to water Arrehnius neutralization: Hydroxide base, general form what’s actually happening? H+ + OH- H2O Salt = the ______________ from the acid ……+ the ______________ from the base Examples with a hydroxide base NaOH+ HCl NaCl + H2O 3H2SO4+ 2Al(OH)3Al2(SO4)3+ 6H2O Arrehnius neutralization: carbonate base, general form what’s actually happening? 2H++ CO32-H2CO3 H2CO3 H2O + CO2 Salt = the ______________ from the acid . . …+ the ______________ from the base Examples with a carbonate base CaCO3 + 2 HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 H2SO4 + NaHCO3 Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2 Acid Strength Compare the difference in these two statements: 1) The more H+ ions in the water, the more ______________ the solution 2) The more H+ ions a compound produces, the ______________ the acid Strong acids release all of their H+ ions Strong acids are ______________ electrolytes Weak acids hold on to ______________ of their H+ ions Weak acids are ______________ electrolytes Weak acids reach ______________ with “______________” products Don't get confused! A solution of a ______________ acid can be less acidic that a solution of a ______________ acid! IF: the strong acid solution is ______________ ______________ and the weak acid is ______________!