Acids, Bases and Salts
advertisement

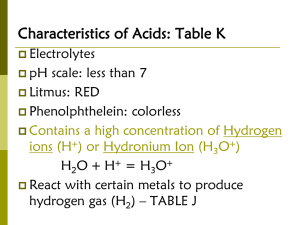
Acids, Bases and Salts Arrhenius definition of acids and bases: Acid: a chemical compound that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution Base: a substance that increases the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH -) in aqueous solution Brønsted- Lowry definition of acids and bases: Acid: a molecule or an ion that is a proton donor Base: a molecule or an ion that is a proton acceptor Lewis definition of acids and bases: Acid: atom, ion or molecule that accepts an electron pair to form a covalent bond Base: atom, ion or molecule that donates an electron pair to form a covalent bond Properties of Acids substances that produces hydrogen ions (H+) in solution - combine with water and become hydronium ions (H3O+) Acids: HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl taste sour are electrolytes are corrosive react w/ indicators to produce a color change indicator – organic compound that changes color in an acid or base (phenolphthalein) Common acids – 4 most important industrial acids: 1. sulfuric acid – car batteries, fertilizers 2. phosphoric acid – detergents, fertilizers 3. nitric acid – fertilizers, explosives (TNT = trinitrotoluene) 4. hydrochloric acid (muriatic acid)- cleaner, gastric juices Properties of Bases substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution Bases: NaOH + H2O → Na+ + OH feel slippery taste bitter are electrolytes are corrosive react w/ indicators to produce a color change Common bases – 1. ammonia (NH3) – most widely used – cleaners, fertilizers, rayon/nylon production NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH- → NH4OH 2. calcium hydroxide – “caustic lime” used to make mortar and plaster 3. sodium hydroxide “lye” used to make soap, drain cleaner Strength of acids and bases: Strong Acid: acid that ionizes almost completely in solution (electrolytes) HCl(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Cl- (aq) Weak Acid: acid that partially ionizes in solution (weak -non electrolytes) CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l) ↔ H3O+(aq) + Cl- (aq) Strong Base: dissociates completely in solution (alkaline) NaOH + H2O(l) → Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Weak Base: partly dissociates in solution NH3(g) + H2O(l) ↔ NH4+(aq) + OH- (aq) Strength Strong Acid HCl, H2SO4, HNO3 Weak CH3COOH, H2CO3, H3BO3 Base NaOH, KOH, LiOH, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 NH3, Al(OH)3, Fe(OH)3 pH = measure of the concentration of hydronium ions in solution pH < 7 = acid pH = 7 = neutral pH > 7 = base Neutralization reactions: chemical reaction between an acid and a base. (produces water and a salt) H3O+ + OH- 2H2O Salt: compound formed when the negative ion from an acid combine with positive ions from a base (any ionic formula). HCl(g) + NaOH(aq) H3O+(aq) + Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + OH-(aq) Water formation: H3O+ + OH-(aq) 2H2O Salt formation: Na+ + Cl- NaCl Common Salts: Sodium chloride (NaCl): table salt Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3): baking soda Calcium carbonate (CaCO3): calcite/chalk Potassium nitrate (KNO3): saltpeter Titration: process in which a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of another solution Known concentration: standard: added to unknown with indicator Endpoint: when one drop of standard causes a color change; usually pink (phenolphthalein used)