Earth's Dynamic Crust & Interior: Notes on Geology
advertisement

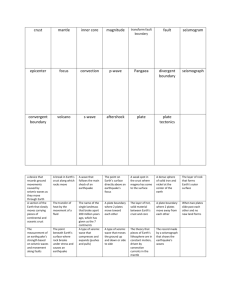
Topic 12 Earth’s Dynamic Crust and Interior Lithosphere: Crust: Small Scale Crustal Changes Law of Original Horizontality: What are three ways that rock layers are changed? 1) 2) 3) 4) Earthquakes and Igneous Activity, Including Volcanoes Earthquake: The stored energy in the ground is released as seismic waves Focus: Epicenter: Fault: Seismograph: Seismogram: 3 Types of Earthquake Waves 1) 2) 3) Properties of Seismic Waves Location of an Epicenter The epicenter of any earthquake can be found by knowing the distance from the epicenter to three seismic stations Process 1) 2) 3) 4) What does the distance from one seismograph tell us? What does the distance from two seismographs tell us? What does the distance from three seismographs tell us? Finding the Origin Time of Earthquakes 1) 2) Magnitude of Earthquakes Measure of the intensity of an earthquake Mercalli Scale: Richter Scale: Tsunami: Igneous Activity and Volcanoes Volcano: Volcanic Eruption: Zones of Crustal Activity Ring of fire: Where are other areas of activity located? A Model of Earth’s Interior Scientists use seismic waves to create a model What happens to pressure from the crust to core? What happens to temperature from crust to core? Zones of the Earth Lithosphere Thinnest layer (shell on a hard boiled egg) 2 Types of crust 1) Continental Crust: Composition: Density: 2) Oceanic Crust: Composition: Density: *Continental Crust is Much Thicker* Moho: Asthenosphere: Mantle: Thickest layer 80% of Earth’s volume Core: 2 Cores 1) Outer Core Composition: State of matter: 2) Inner Core Composition: State of matter: Plate Tectonic Theory What is a plate? The lithosphere of the earth is made up of 12 major plates How fast do these plates move? Evidence of Plate Tectonics Fossils: Geology: Puzzle: The Driving Force Behind Plate Movement The Three Types of Plate Boundaries 1) Divergent: a.) Midocean ridges: b.) Rift Valleys: 2) Convergent: 3 Varieties of Convergence a.) Oceanic-Oceanic: b.) Oceanic-Continental: - c.) Continent-Continent: 3.) Transform Plate Boundaries: - Hot Spots: -Ex.: Effects of Plate Tectonics Appearance of Continents: Features of Landmasses: Age and Heat Patterns Age: Heat Patterns: Magnetic Patterns -