File
advertisement

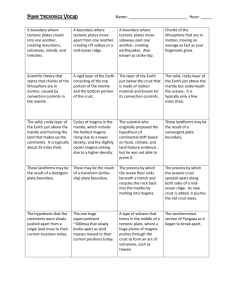
asthenosphere The “plastic” (semisolid) layer of Earth below the lithosphere; part of the upper mantle convection current The movement of the mantle, which pushes the plates around core the iron-and-nickel center of Earth crust the outermost shell of the Earth; the upper part of the lithosphere inner core the innermost part of the Earth; solid nickel and iron lithosphere the solid, outermost shell of the Earth includes the crust and upper mantle mantle the thick layer of Earth between the crust and the core outer core the liquid portion of the core plates one of the 15 major segments that make up Earth’s lithosphere Continental Drift A theory proposed by Alfred Wegner which states the continents are moving away from each other convergent boundary boundary between 2 plates moving together boundaries between two plates divergent boundary that are moving apart fault a fracture in the Earth’s crust A chain of volcanic mountains that are Mid-Atlantic Ridge the site of seafloor spreading under the Atlantic Ocean Plate Tectonics Theory the theory that the outer part of the earth is made up of rigid plates that move relative to each other Seafloor Spreading the process by which oceanic plates diverge (move apart) allowing magma to fill the void and create a new seafloor subduction a type of convergent boundary where a plate slides underneath another plate transform boundary boundary where the plates move past each other in opposite directions earthquake a sudden trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy caused by plate movement. Common around plate boundaries and faults epicenter the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake focus the point of origin of an earthquake seismic waves waves generated by an earthquake in all directions seismograph an instrument that detects, records, and measures vibrations produced by earthquakes seismologists scientists who study earthquakes hot spots a very hot area underneath the crust. As a plate slowly passes above it, magma melts the crust creating chains of volcanoes lava molten rock on the surface of the Earth magma molten rock underground ring of fire many volcanoes and earthquakes happen where plates meet around the Pacific Ocean shield volcano a large, broad, and flat type of volcano stratovolcano a steep sided volcano viscosity the thickness or thinness of lava or magma fossils the remains or imprints in rock of things that lived long ago a timeline that represents the entire history of the geologic time scale Earth since its formation geology the study of the Earth pangea the name of the one huge continent that means “all lands”