Student
advertisement

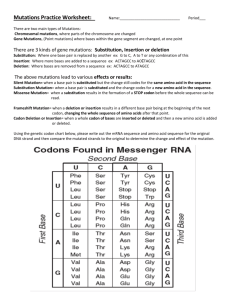
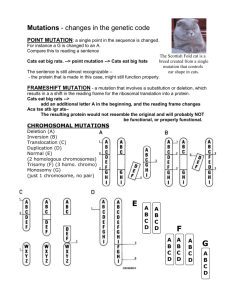
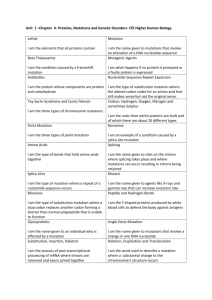
Station 10 2D DNA Mutations and Change 1. Using the genetic code chart, compare the first part of the DNA strand to the second part. Do this by circling the bases by groups of three, forming codons, and comparing the codons as to which one changed. Find the resulting amino acid change (may not matter, may have catastrophic results) 2. Look at the four different karyotypes on the following pages and circle the abnormal chromosomes (anomaly) 5’ AUGUCGCAA 3’ 5’ AUAUCGCAA 3’ 5’ AGCGUCUAG 3’ 5’ AGCGUCUAU 3’ 5’ GUGCGAUUU 3’ 5’ GUGGGAUUU 3’ 5’ ACGGCUACC 3’ 5’ ACGGGUACC 3’ Changes to the Genetic Code 1. Arrange the colored letters in the order shown below. Note that the letters are arranged in groups of three which represent a codon. Determine the name of the amino acid each codon represents using the mRNA Genetic Code chart. Write the name of the amino acids on your student answer sheet. 2. Genetic mutations are often caused by changes in the bases of the codons. Compare the sequence of codons above to the sequence below and find the change that has occurred in one of the codons. What amino acid has been changed? What is the new amino acid? This type of mutation is called a point mutation. One base changed but resulted in a different amino acid. Write the new codon arrangement on your answer sheet and identify the amino acid sequence. 3. Using the original codon sequence in question 1, add one additional cytosine before the second codon, GCG. Now shift the remainder of the bases into new codon groups of three bases. You will have one base left over at the end. How have the amino acids changed from the original sequence? This is called a frame-shift mutation known as insertion. Write the new codon arrangement on your answer sheet and identify the amino acid sequence. 4. Using the original codon sequence in question 1, remove a base from the first codon, AUG. Rearrange the bases into new codons with three bases for each codon. How have the amino acids changed from the original sequence? This is a frame-shift mutation know as deletion. Write the new codon arrangement on your answer sheet and identify the amino acid sequence. Using the genetic mutation cards, read each card carefully and determine the cause of the mutation. Place a check mark in the appropriate column to indicate the type of genetic mutation Described and illustrated on each card. Justify your response in the space provided and decide whether this is a good or bad mutation. 1 Type of Mutation: Alpha Antitrypsin Deficiency Point Mutation Deletion Insertion Polyploidy Justify your answer: Type of Mutation: Strawberries 2 Point Mutation Justify your answer: Deletion Insertion Polyploidy 3 Type of Mutation: Huntington’s Disease Point Mutation Deletion Insertion Polyploidy Justify your answer: 4 Type of Mutation: Sickle Cell Anemia Point Mutation Deletion Insertion Polyploidy Justify your answer: Type of Mutation: Cystic Fibrosis 5 Point Mutation Justify your answer: Deletion Insertion Polyploidy Type of Mutation: Orchid 6 Point Mutation Deletion Insertion Polyploidy Justify your answer 7 Type of Mutation: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Point Mutation Deletion Insertion Polyploidy Justify your answer Type of Mutation: Tay-Sachs 8 Point Mutation Justify your answer Deletion Insertion Polyploidy