Teacher
advertisement

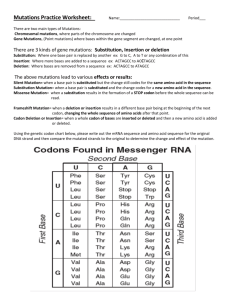
Station 10 2D Describe the relationships between changes in DNA and potential appearance of new traits including Alterations during replication Insertions Deletions Substitutions Mutagenic factors that can alter DNA 5’ AUGUCGCAA 3’ 5’ AUAUCGCAA 3’ 5’ AGCGUCUAG 3’ 5’ AGCGUCUAU 3’ 5’ GUGCGAUUU 3’ 5’ GUGGGAUUU 3’ 5’ ACGGCUACC 3’ 5’ ACGGGUACC 3’ A A A A A A A A A A U U U U U U G G G G G G C C C C C C C C C G U A Changes to the Genetic Code 1. Arrange the colored letters in the order shown below. Note that the letters are arranged in groups of three which represent a codon. Determine the name of the amino acid each codon represents using the mRNA Genetic Code chart. Write the name of the amino acids on your student answer sheet. 2. Genetic mutations are often caused by changes in the bases of the codons. Compare the sequence of codons above to the sequence below and find the change that has occurred in one of the codons. What amino acid has been changed? What is the new amino acid? This type of mutation is called a point mutation. One base changed but resulted in a different amino acid. Write the new codon arrangement on your answer sheet and identify the amino acid sequence. 3. Using the original codon sequence in question 1, add one additional cytosine before the second codon, GCG. Now shift the remainder of the bases into new codon groups of three bases. You will have one base left over at the end. How have the amino acids changed from the original sequence? This is called a frame-shift mutation known as insertion. Write the new codon arrangement on your answer sheet and identify the amino acid sequence. 4. Using the original codon sequence in question 1, remove a base from the first codon, AUG. Rearrange the bases into new codons with three bases for each codon. How have the amino acids changed from the original sequence? This is a frame-shift mutation know as deletion. Write the new codon arrangement on your answer sheet and identify the amino acid sequence. Sickle cell anemia is the result of a point mutation, a change in just one amino acid in the gene for hemoglobin. The mutation causes red blood cells to become rigid and sickle-shaped, which can lead to lung tissue damage, pain episodes, stroke and damage to most organs including the spleen, kidneys and liver. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and there is currently no cure available. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy results from a mutation caused by the deletion of DNA bases that lead to errors in the translation and loss of the production of the dystrophin protein. The lack of dystrophin, An important protein in skeletal muscles, leads to severe muscle weakness and eventually death. Huntington's disease is a disorder in which nerve cells in certain parts of the brain waste away, or degenerate. A CAG repeat occurs many more times than it is supposed to. Normally, this section of DNA is repeated 10 to 28 times. Strawberries that are Polyploid have multiple sets of chromosomes. Mutations such as this have positive effects and are not harmful. Alpha1 Antitrypsin Deficiency is caused by a single point mutation that results in rare form of emphysema in adults and a rare form of liver disease (cirrhosis) in children and adults. The liver does not make enough of a protein that protects the lungs and liver from damage Cystic Fibrosis is a disease that causes thick, sticky mucus to form in the lungs, pancreas and other organs. In the lungs, mucus blocks airways, causing lung damage and making it hard to breathe. In the pancreas, it clogs the pathways leading to the digestive system, interfering with proper digestion. The disorder is caused by the deletion of three bases which prevents phenylalanine in the cell membrane. Tay-Sachs disease is a rare disorder that results in the destruction of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. The disorder is caused by an addition of base pairs that alter the coding of the mRNA sequence and causes problems in lysosomes, the waste processing centers of the cell. Polyploidy in orchids result in larger flowers. This type of orchid has twice the number of chromosomes as found in other orchids.