Inheritance and Genetics

Lesson Outline for Teaching
Lesson 1: Inheritance and Traits
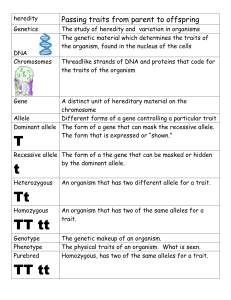
gene section of DNA that has genetic information for one trait genotype organism’s complete set of genes inheritance passing of traits from generation to generation mutation permanent change in the sequence of DNA in a gene phenotype how a trait appears or is expressed population all the members of a species living in a given area random without a definite aim, rule, or method trait distinguishing characteristic of an organism
A.
What is inheritance?
1.
A(n) trait is a distinguishing characteristic of an organism.
2.
The passing of traits from generation to generation is called inheritance.
3.
A trait that an organism acquires or develops during its lifetime is called a(n) acquired trait.
B.
Inheritance and DNA
1.
Amoebas, bacteria, and some plants pass traits to their offspring by cell division and mitosis, a process called asexual reproduction.
2 .
Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are identical to the original organism.
3 .
Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are similar to but not identical to the parent or parents.
4 .
Sexual reproduction requires DNA from a(n) sperm cell and an egg cell.
5 . DNA is a molecule inside a cell’s nucleus that looks like a twisted zipper.
a.
A section of DNA that has genetic information for one trait is called a(n) gene. b.
A(n) chromosome is a structure made of long chains of DNA.
6.
In most species, chromosomes come in pairs.
a.
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each body cell. b.
Human sperm and eggs, or reproductive cells, each contain 23 single chromosomes.
C.
Combining Genes
1 .
During sexual reproduction, an egg cell and a(n) sperm cell each contribute one gene for a trait.
2 .
Each gene for a single trait is called a(n) allele.
3 .
The process in which sperm and egg cells form is called meiosis. a.
During meiosis, the chromosomes in existing egg and sperm cells replicate and divide. b.
Meiosis results in four separate cells, each with half the number of chromosomes the original cells had.
4 .
During fertilization, egg cell chromosomes and the sperm cell chromosomes combine to form an offspring with a full set of paired chromosomes.
5 .
Each offspring resulting from sexual reproduction is unique because each sperm cell and egg cell is unique.
D.
Influencing Traits
1. An organism’s genotype is its complete set of genes.
2. The traits expressed by the genotype can be influenced by an organism’s environment.
3. How a trait appears, or is expressed, is called the trait’s phenotype. a.
Phenotypes result from the interaction between an organism’s genes and its environment. b.
Nutrients can cause dramatic changes in the phenotypes of plants and animals. c.
An organism’s social group also can affect color, body structure, or behavior.
4.
A change in phenotype in response to environment does not affect an organism’s genes and the change is not passed on to future generations.
5.
A permanent change in the sequence of DNA in a gene is called a(n) mutation. a.
A mutation in a gene can change the trait for which the gene holds information. b.
All genes can mutate, but only mutated genes in egg or sperm cells can be inherited.
6.
Many mutations do not help or hurt an organism.
7. Mutations that change an organism’s genes so much that they can affect an organism’s ability to survive in its environment can be harmful or helpful.
Lesson 2: Adaptations in Species
adaptation inherited trait that helps a species survive in its environment camouflage adaptation that helps a species blend in with its natural surroundings mimicry adaptation in which one species looks like another species natural selection process by which organisms with variations that help them survive in their environment live longer, compete better, and reproduce more than those that do not have the variation selective breeding selection and breeding of organisms with desired traits species group of organisms that share similar characteristics and can reproduce among themselves, producing fertile offspring variation slight difference in inherited traits among individual members of a species
A.
What is adaptation?
1.
Variations are slight differences in inherited traits among individual members of a species.
2.
Variations occur through mutations, which can be harmful, not harmful, or beneficial.
3.
An inherited trait that helps a species survive in its environment is called a(n) adaptation.
B.
How Adaptations Occur
1 .
The process by which organisms with variations that help them survive in their environment live longer, compete better, and reproduce more than those that do not have the variation is called natural selection.
a.
A variation that helps an organism survive or compete better in its environment enables the organism with that variation to live longer. b.
An organism that lives longer tends to have more offspring that also can have the variation. c.
Over many generations, more and more offspring inherit a beneficial variation. d.
Once most of a population have a beneficial variation, it becomes a(n) adaptation.
2 .
New variations are random and occur continually because mutations are random and occur continually.
3 .
When an environment changes, a population must adapt through natural selection or it will die off.
4 .
Selective breeding is the selection and breeding of organisms that have desired traits.
5 .
Selective breeding is similar to natural selection except, instead of nature, humans do the selecting.
C.
Types of Adaptations
1.
Adaptations enable species to maintain homeostasis, avoid predators, find and eat food, and move.
2.
The three main categories of adaptations are structural, behavioral, and functional. a.
A structural adaptation is a(n) physical trait, such as color, shape, or internal structure, that increases survival. b.
A behavioral adaptation is a behavior or action, such as migration, hibernation, hunting at night, or playing dead that increases survival. c.
A functional adaptation is a(n) biochemical change, such as hibernating, shedding, or spitting that enables a species to increase survival or maintain homeostasis.
3 .
Homeostasis is the ability of an organism to keep its internal conditions within certain limits.
4 .
Adaptations that protect organisms from predators include variations that make an organism resemble something else.
a.
Adaptations that enable a species to blend in with its environment are called camouflage. b.
An adaptation in which one species looks like another species is called mimicry.
5 .
Adaptations such as camouflage and mimicry that protect species from predators can also help species find food.
6 .
Some plants have adaptations such as modified underground stems that enable them to store food.
7 .
Adaptations that help species move include legs, wings, flippers, fins, and tails.
8 .
Movement helps species search for food, avoid predators, and escape unpleasant stimuli.