Heredity Test Review Sheet - 7th Grade Science
advertisement

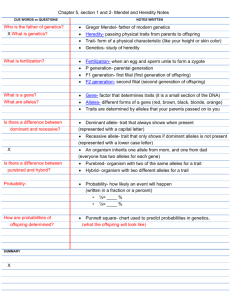
Chapter 4: Heredity Test Review Sheet 7th Science Vocabulary to know: Heredity-the passage of genetic instructions form one generation to the next Traits- the physical characteristics that are studied in genetics Allele- the different forms of a gene Phenotype- an organism’s physical appearance or visible traits (ex. tall stems) Genotype- an organism’s genetic makeup (ex. Tt) Dominant allele- an allele whose trait always shows up (ex. P) Recessive allele- an allele whose trait can be hidden (ex. p) Homozygous- an organism that has 2 identical alleles for a trait (ex. PP or pp) Heterozygous- an organism that has 2 different alleles for a trait (ex. Pp) Hybrid- an organism that has 2 different alleles for a trait (heterozygous) Purebred- an organism that has the same form of a trait (homozygous) Probability and Heredity Be able to create and interpret a Punnett square for a given scenario. (Look back at notes in ISN or Spongebob Squarepants sheets.) Patterns of Inheritance Codominance- occurs when both alleles for a gene are expressed equally. For example, a chicken with black feathers FBFB and a chicken with white feathers FWFW will have offspring that have both black and white feathers (FBFW). Polygenetic inheritance-occurs when more than one gene affects a trait Chromosomes and Inheritance Chormosome theory of inheritance- genes pass from parents to their offspring on chromosomes. Meiosis is the process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half as sex cells form. In meiosis the chromosome pairs separate and are distributed into new sex cells. Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction: Involves 2 parents Involves joining of the sperm and egg Different offspring of the same parents can have different characteristics Asexual reproduction: One parent produces a new organism identical to itself