Electronic Supplementary Material
advertisement

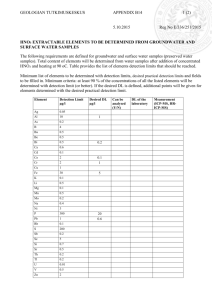
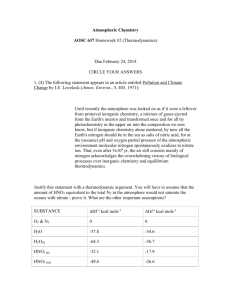
Electronic Supplementary Material A composite prepared from halloysite nanotubes and magnetite (Fe3O4) as a new magnetic sorbent for the preconcentration of cadmium(II) prior to its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry Mohammad Amjadi*, Azam Samadi and Jamshid L. Manzoori Faculty of Chemistry, University of Tabriz, Tabriz 5166616471, Iran * Corresponding author, Email: amjadi@tabrizu.ac.ir, Tel: +984133393109; Fax: +984133340191 Optimization of MSPE procedure pH is a very important factor for Cd-phen complex formation and also for its adsorption on HNTs-Fe3O4. The effect of pH on the adsorption of Cd-phen complex on HNTs-Fe3O4 as well as on HNTs and Fe3O4 was studied. As shown in Fig.S1a, Fe3O4 nanoparticles exhibited no quantitative adsorption for Cd-phen complex at pH range of 2-10. When the pH was above 7.0, the adsorption amount increased and reached a maximum at pH 10. This can be attributed to the fact that the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles was negatively charged when the pH value was above the point of zero charge (6.5) and the (Cd(phen)32+) was better adsorbed onto the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. For HNTs-Fe3O4, a recovery of > 95 % was obtained at the pH range of 5.0–9.0 and the behavior of magnetic sorbent was similar to HNTs. The surface of HNTs is mostly negative at pH 2–12 due to the negative potential of outer-most SiO2 with a small contribution from the positive inner cylinder surface Al2O3 [20]. With increasing the pH value, the surface of HNTs becomes more negatively charged, thereby increasing the electrostatic attraction between positively charged Cd-phen complex and negatively charged surface sites and causing an increase in Cd-phen complex uptake. So, pH 6.0 was chosen as the optimum pH for further studies. To adjust the pH, different buffers such as ammonium acetate, phosphate, sodium acetate and ammonium citrate were tested and no difference was seen between them. Therefore, phosphate buffer was chosen for adjusting pH. The effect of the ligand amount on the retention of the analyte ions on the sorbent was also examined. The results are given in Fig. S1b. The recovery of cadmium increased with increasing the amount of phen and reached a constant value with at least 1.0 mL of 0.3 % phen solution. However, because of the possible consumption of ligand by other cations in real samples, 3 mL of ligand solution was selected for further studies. It should be mentioned that without complexation with phen, no quantitative recovery was obtained for Cd ions. The effect of sample volume on the recovery of 2.0 µg of Cd(II) with HNT–Fe3O4 was studied in the range 50–500 mL. As seen from Fig. S1c, the recovery decreases when the volume was higher than 100 mL. Therefore, 100 mL was considered to be the maximum sample volume. The time of sonication was varied from 2 to 15 min during the preconcentration of 2.0 µg of Cd(II) in 100 mL of solution by using HNT–Fe3O4. The obtained results shown in Fig. S1d, indicated that a 5-min sonication time was sufficient for adsorption of Cd(II) by HNT–Fe3O4. Elution of Cd(II)-phen complex from magnetic HNTs was performed by using HCl and HNO3 as common eluents. The obtained results showed that HNO3 is better eluent because of better reproducibility and higher recovery. Hence, the effect of HNO3 volume and concentration on the recovery of analyte was studied (Table S1). Complete recoveries were obtained by 2.0 mL of 0.1 M HNO3. In order to achieve complete desorption of analyte, sorbent was sonicated for 60 s during desorption process. Table S1. Effect of eluent type, concentration and volume on the recovery of Cd(II), pH=6.0. Eluent type Recovery (%) 1.0 mL HNO3 (5.0 M) 70 2.0 mL HNO3 (5.0 M) 100 2.0 mL HNO3 (1.0 M) 100 2.0 mL HNO3 (0.1 M) 100 2.0 mL HCl (1.0 M) 92 Fig. S1. Effect of (a) pH of sample solution on the analyte recovery; Cd: 40 μg L−1, sample volume: 50 mL, eluent: 2mL HNO3 2M (b) concentration of phen on the adsorption of the Cd(II) ions; pH:6.0, sample volume: 50 mL, eluent: 2mL HNO3 2M (c) volume of sample on analyte recovery; Cd: 2 µg, pH: 6, eluent: 2 mL HNO3 2M (d) time of sonication, conditions are as in c.