hw_04_sol
advertisement

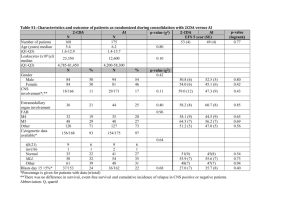
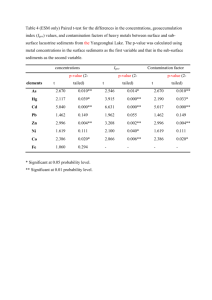
Homework 4 Covers Chapters 7 and 8 Use the Project Talent data set. 1. Perform a multiple regression by regressing Math on Gender, SES, Sociability, Reading, and Mechanical Reasoning entering the predictors in this order. a. What is the interpretation of the t-tests for SES and Sociability? Be sure to include the null and alternative hypothesis being tested, the degrees of freedom, the pvalue, and your conclusion and decision about Ho at a 10% level of significance. SES Ho: B2 = 0 Ha: B2 ≠ 0 t-stat: 1.63 DF: 19 p-value: 0.119 Decision/Conclusion: Since p-value is greater than 0.10 we would not reject Ho. Plausible that the addition of SES makes no significant linear contribution to prediction of Math Achievement when Gender, Sociability, Reading, and Mechanical Reasoning are in the model. Sociability Ho: B3 = 0 Ha: B3 ≠ 0 t-stat: - 0.11 DF: 19 p-value: 0.912 Decision/Conclusion: Since p-value is greater than 0.10 we would not reject Ho. Plausible that the addition of Sociability makes no significant linear contribution to prediction of Math Achievement when Gender, SES, Reading, and Mechanical Reasoning are in the model. Regression Analysis: Math versus Gender, SES, Social, Reading, Mech The regression equation is Math = - 19.4 - 0.63 Gender + 0.231 SES - 0.050 Social + 0.237 Reading + 1.28 Mech Predictor Constant Gender Coef -19.36 -0.635 SE Coef 14.14 3.101 T -1.37 -0.20 P 0.187 0.840 1 SES Social Reading Mech 0.2312 -0.0501 0.2370 1.2820 0.1415 0.4476 0.1826 0.4641 1.63 -0.11 1.30 2.76 0.119 0.912 0.210 0.012 b. State the null and alternative hypotheses being tested by the ANOVA table in output. Include the F-statistic, p-value, and your decision and conclusion about Ho. Ho: All slopes equal 0 Ha: Not all slopes equal 0 F-stat: 8.83 p-value: 0.000 Decision/Conclusion: Reject Ho and conclude at least one slope does not equal 0. Analysis of Variance Source Regression Residual Error Total Source Gender SES Social Reading Mech DF 1 1 1 1 1 DF 5 19 24 SS 1769.93 761.91 2531.84 MS 353.99 40.10 F 8.83 P 0.000 Seq SS 401.28 582.95 48.57 431.08 306.04 c. Use the Sequential SS to conduct the following partial F tests. Be sure to include the null and alternative hypotheses being tested, the degrees of Freedom, the pvalue from both the F-table in text (this will be a range) and by using Calc > Probability Distributions in Minitab, and your conclusion and decision about Ho at 10% level of significance. Reading and Mechanical Reasoning to model with Gender, SES, and Sociability Ho: B4= B5= 0 (both slopes are 0) Ha: at least one of these two slopes does not equal 0. F-stat: F = (431.08+ 306.04 / 2 368.56 = = 9.19 (761.91) /19 40.10 DF: 2, 19 p-value from table: 0.001< p < 0.005 p-value from Minitab: 0.0016 Decision/Conclusion: Since p-value is less than 0.10 we reject Ho and conclude that at least one of these predictors, Reading and Mechanical Reasoning, is a significant 2 linear predictor of Math Achievement when Gender, SES, and Sociability are in model. Reading to model with Gender, SES, and Sociability Ho: B4= 0 Ha: B4 ≠ 0 F-stat: F 431.08 / 1 431.08 8.07 (761.91 306.04) / 20 53.40 DF: 1, 20 p-value from table: 0.01 < p < 0.025 p-value from Minitab: 0.0102 Decision/Conclusion: Since p-value is less than 0.10 we reject Ho and conclude that Reading is a significant linear predictor of Math Achievement when Gender, SES and Sociability are in model. d. Compute the partial coefficient of determination (i.e. partial R2) and partial correlation for adding Mechanical Reasoning to model already containing Gender, SES, Sociability and Reading. Be sure to correctly identify the direction of this correlation. Partial r: 0.535 Partial R2: 28.6% Interpretation: This indicates that the effect of Mechanical Reasoning in reducing the variability in Math Achievement when Gender, SES, Sociability, and Reading are already in the model is 28.6% e. Use Minitab > Basic Statistics > Correlation to get the correlation matrix of the six variables. Which variable has the strongest relationship with Math Achievement? The weakest? Strongest: Mechanical Reasoning (r = 0.797 Weakest: Sociability (r = - 0.219) f. Compute the test statistic to determine whether the correlation between Math Achievement and Sociability in the population is equal to zero with a two-tailed test and alpha of 5%. Use Minitab Calc > Probability Distributions to get p-value. Check your conclusion (i.e. p-value) to that found in the correlation matrix of part e. 3 Ho: p = 0 Ha: p ≠ 0 t-stat: t = r√(n-2)/ √(1-r2) = -0.219√(25-2)/ √(1-(-0.2192)) = - 1.076 DF: 23 p-value: 0.292 Decision/Conclusion: Since p-value is greater than 0.05 we would fail to reject Ho and conclude that the population correlation between Math Achievement and Sociability is not different from 0. g. Compute the 95% confidence interval for the correlation between Reading and Sociability. Remember to transform your interval back from the Fisher’s value to the population correlation using Table B8. z ' z(1 / 2) z ' z (1 / 2) n 3 where z’ = (n 3) 0.325 1 1 r12 ln 2 1 r12 where z ' 1 1 r 1 1 (0.317) 0.325 ln ln 2 1 r 2 1 (0.317) 1.96 0.325 0.418 0.743 z ' 0.093 (25 3) From Table B8 this converts to 0.63 p 0.09 Since this interval contains 0 we would fail to reject Ho at the 5% level of significance. h. How would you interpret the correlation between Gender and Mechanical Reasoning (remember that Males were coded as 0 and Females as 1). How could we have made this correlation positive? The correlation of – 0.528 implies that Males scored higher on Mechanical Reasoning than Females (i.e as the value of Gender increased from 0 to 1 the Mechanical Reasoning scores decreased). If one wanted to change the direction you could simply recode Females as 0 and Males as 1. 2. The variable School Size is interpreted as follows: 1 = number of students is less than 100 2 = number of students is from 100 to 399 3 = number of students is 400 or more A lack-of-fit test regressing Math on Gender, SES, Sociability, Reading, Mechanical Reasoning, and School Size indicates that a possible curvature exists for the variables 4 Reading and Mechanical Reasoning. Without centering, create new, second-order variables for Reading and for Mechanical Reasoning. Repeat the multiple regression analysis including these second order terms. Select Options and select Variance Inflation Factor and Lack-of-Fit > Data Subsetting and answer the following questions. a. What are the VIF values for all of the predictors? Predictor Constant Gender Reading Mech Social SES School_Size Reading2 Mech2 Coef 12.255 -0.955 -1.1096 -2.4246 0.5326 0.12741 2.9210 0.02624 0.17232 SE Coef 8.689 1.557 0.5938 0.9587 0.2436 0.08062 0.9586 0.01083 0.05258 T 1.41 -0.61 -1.87 -2.53 2.19 1.58 3.05 2.42 3.28 P 0.178 0.548 0.080 0.022 0.044 0.134 0.008 0.028 0.005 VIF 1.547 68.549 44.186 1.366 1.836 1.316 76.321 54.056 b. Does this indicate the presence of Multicollinearity? Why or why not? Yes, since the VIF are greater than 10 for the first and second order terms c. What is the p-value of the lack-of-fit tests and what does this indicate about model fit? P >= 0.1 so no evidence of lack of fit. 3. Create new second order terms for Reading and Mechanical Reasoning after centering both the first order terms. Repeat the multiple regression analysis including these centered first and second order terms. Select Options and select Variance Inflation Factor and Lack-of-Fit > Data Subsetting and answer the following questions. a. What are the VIF values for all of the predictors? Predictor Constant Gender Social SES School_Size cReading cMech cReading2 cMech2 Coef -2.591 -0.955 0.5326 0.12741 2.9210 0.5045 1.4354 0.02624 0.17232 SE Coef 7.368 1.557 0.2436 0.08062 0.9586 0.1214 0.3610 0.01083 0.05258 T -0.35 -0.61 2.19 1.58 3.05 4.15 3.98 2.42 3.28 P 0.730 0.548 0.044 0.134 0.008 0.001 0.001 0.028 0.005 VIF 1.547 1.366 1.836 1.316 2.867 6.264 2.895 3.047 b. Does this indicate the presence of Multicollinearity and support your answer? No, there are no VIF values greater than 10 c. What is the p-value of the lack-of-fit test and what does this indicate about model fit? P >= 0.1 so no evidence of lack of fit. 5