Biodiversity SLO # 3.1.1 : Biodiversity : It is variation of life forms
advertisement

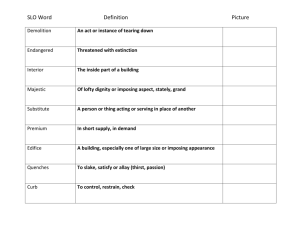
Biodiversity SLO # 3.1.1 : Biodiversity : It is variation of life forms within ecosystem or on the earth. It also refers to the variety or variation of living organisms. Example : Unicellular and Multicellular is the example of biodiversity present on the earth. SLO # 3.1.2 : Animals, Plants, Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, Fungi and Algae. Eukaryotes : Organism made up of cell which contain nuclear membrane. Example : Human being and Animals. Prokaryotes : Organism made up of cell which doesn’t contain nuclear membrane. Example : Bacteria and Cyano bacteria. SLO # 3.1.3 : By biodiversity we can study more easily. We can know about how to fertilize soil. We can know about from which organism we can get food. We get information that we can use dung of cow as fuel. We can maintain our ecosystem such as N2 and O2. We get that we can use organisms in industry such as yeast and poison. SLO # 3.2.1 : Basis of Classification and Taxonomy : Morphology : The study of external structure of living organism. Anatomy : The study of internal structure of living organism. Homology : The study of organ structure same but function different. Analogy : The study of function same but structure different. Embryology : The study of growth of zygote into embryo. Example : Human arm, whale flapper and wings of bird. SLO # 3.2.2 : Aims and Principles of Classification : There is large number of organisms found on earth. To study such a large collection, biologists divided organisms into groups and sub groups. It determine similarities and differences among organisms so that we can learn more easily and to find the evolutionary relationship among organisms. SLO # 3.3.1 : Aristotle contributed in the classification of living organism as the founder of biological classification by classifying all living organisms into two main groups Plantae and Animalia. He also wrote book named de Anima (on the soul) on the animals. SLO # 3.3.2 : Bases For Five Kingdom Classification : The levels of cellular organization like prokaryotic, unicellular eukaryotic and multicellular eukaryotic. The principal modes of nutrition like photosynthesis, absorption and ingestion. The genetics levels were also considered as the base of five kingdom classification. SLO # 3.3.3 : Two Kingdom Classification It has only two kingdoms. The base of classification is only Nutrition. No concept of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is introduced by Aristotle and improved by Carolus Linnaeus. Function and structure of animals and plants are same. Example : Kingdom Plantae and Animalia. Five Kingdom Classification It has five kingdoms. The base of classification is Cytology, Anatomy etc. Concept of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is introduced by Robert Whittaker and improved by Margulis and Schwartz. Function and structure of animals and plants are same. Example : Kingdom Monera, Protista, Plantae, Fungi and Animalia. SLO # 3.3.4 : Five kingdom classification system explains all types of living organism present on the earth than two kingdom classification. Two kingdom classification only tells about plants and animals but five kingdom classification tells about all organisms such as fungi, algae and eukaryotes. SLO # 3.3.5 : Abu Usman Umer Aljahiz contributed the characteristics of 350 species of animals in his book and wrote a book on Ant’s life. SLO # 3.4.1 : Kingdom : A kingdom is a group of related phylum. Phylum : A phylum is a group of related classes. Class : A class is a group of related orders. Order : An order is a group of related families. Family : A family is a group of related genera. Genus : A genus is a group of related species. Species : A species consists of similar organisms. Human Classification Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata / Vertebrates Class Mammalia Order Primates Family Hominidae Genus Homo Species Homo sapiens SLO # 3.5.1 : Characteristics of Kingdom Prokaryotes : They have prokaryotic cells which don’t have true nucleus. Nuclear Membrane is absent here. They have cell wall which is Non-Cellulose. They are Autotrophic and Heterotrophic. They are unicellular. They are also found chains, clusters and colonies. They can perform photosynthesis because they have chlorophyll in their cytoplasm but few can do photosynthesis. Example : Bacteria and Cyanobacteria. SLO # 3.5.2 : Characteristics of Kingdom Protoctista : They have Eukaryotic cells which have true nucleus. Nuclear Membrane is present here. They have cell wall but present in some forms or various types. They are photosynthetic, heterotrophic and combination. They have unicellular and simple multicellular organisms. Example : Algae, Protozoan and Fungi-Like. Algae : They are unicellular, colonial and simple multicellular. They resemble to plant because they have cell wall and chlorophyll. They don’t have multicellular sex organs. They don’t form embryo during their life cycle. Example : Spirogyra is kind of multicellular algae present in water and Chlamydomonas is kind of unicellular algae. Protozoan : They resemble to animals whose cells have lack of chlorophyll and cell wall. Example : Amoeba, Euglena, Ent Amoeba, Plasmodium and Paramecium. Fungi-Like : Those look like fungi. Example : Slime molds SLO # 3.5.3 : Characteristics of Kingdom Fungi : They have Eukaryotic cells. Nuclear Membrane is present here. They have cell wall which is made up of chitin. They are Absorptive Heterotrophic. They live on organic material, secrete digestive enzymes. They haven’t chlorophyll. There are 80000 species of fungi. They are multicellular organisms. They are decomposers which breaks large molecules into small molecules. Their body is composed of Hyphae. Their body is called mycelium. Mitosis takes place here. Sexual and asexual reproduction takes place here. They are also living free which are saperotrophic. Example : Yeast and Mushroom. They are also parasites which depend on other dead organisms for their organisms. Budding also takes place here. They are also used in baking industries like yeast. They are used in medicines like Penecillium Antibiotic. It is also used in brewing industries like fungus. They are spoiling food, human and plant diseases. It is also used in food like Mushroom. Example : Rhyzopus present in bread and also known as bread fungus. SLO # 3.5.4 : Characteristics of Kingdom Plantae : They have Eukaryotic cells. Nuclear Membrane is present here. They have cell wall made up of cellulose and Lignin. They are Autotrophic. They can perform photosynthesis. They have multicellular sex organs. They can form embryo during their life cycle. They are multicellular organisms. They are Aquatic and land plants. Sexual and asexual reproduction takes place here. Example : Mosses and Ferns. They have two types Bryophytes and Tracheophytes. Bryophytes : They don’t consist vascular bundles. Their size is small and only 2 to 3 cm. They are simplest plants. They are present in cool, shadow and damp places. Sexual and asexual reproduction takes place here. They are also known as Amphibians plants. Example : Herbs and shrubs. Tracheophytes : They are vascular plants. They have large sizes. They are found in higher places. Sexual and asexual reproduction takes place here. Example : Moss, Hornworts and Liverworts. Pteridophytes : They are vascular plants. They are seed less plants. They are found in terrestrial, land and hilly areas. They have simple leaf. Sexual and asexual reproduction takes place here. They are neutral season which can grow in any season. They are various in sizes. Example : ferns Spermatopsida : It consist two types Gymnosperms and Angiosperms. Gymnosperms : Gymno : naked Sperm : seed They have seeds without enclosed fruits. They don’t have flower and fruits. They are ever green plants. They are present in colder and higher regions like muree, quetta, gilgit and Hunza. Example : Chilgoza plant, Conifers and Thufa ( Morpankh ). Angiosperms : Angio : enclosed Sperm : seeds They have seeds are covered with fruits. They are the largest group of plants. They are present on most of areas of earth. It has two types Monocotyledon and Dicotyledon. Monocotyledon : They have one cotyledon. Example : Rice, corn, date, barley and palm. Dicotyledon : They have two cotyledon. Example : Apple, mango, grapes, gram and pulses. SLO # 3.5.5 : Characteristics of Kingdom Animalia : They have Eukaryotic cells. Nuclear Membrane is present here. They don’t have cell wall. They are Heterotrophic. They are multicellular organisms. It has two types Vertebrates and Invertebrates. Vertebrates : It has five groups Pieces, Amphibians, Reptiles, Aves and Mammals. Pieces : They are fishes. They have fins, gills and scales on their body. They are aquatic animals. Example : Labeo, Seahorse and Shark. Amphibians : They survive their half life in water and half life on land. Example : Frog, Toad and Selemender. Reptiles : They are creepy animals. Example : Crocodile and Snakes. Aves : They are birds. They have wings and feathers on their body. Example : Sparrow and Parrot. Mammals : They have hairs on their skin and female feed their young one. Example : Human beings Invertebrates : Phylum Name Phylum Porifera Phylum Coelentrates Phylum Nematoda Phylum Annelida Characteristics They have pores on their body. They have special cavity. They are round worms. They have segmented bodies. Phylum Arthropoda They have jointed legs. Phylum Echinodamoda They have spines on their body. Phylum Mollusca They have soft body. Phylum They have flat body. Platyhelminthes Examples Sycon and Sponge Jelly fish and Hydra Hook worm, Round worm and Ascaris Earth worm and Leach Insects and Scorpion Star fish and Sea Urchin Snail and Mussel Tape worm, Liver fluke and Planaria SLO # 3.5.6 : They are between of living and non-living thing. They are a cellular because they don’t have cellular organization. They have DNA or RNA, encased in protein coat. They cause number of diseases in human body. They act as non-living particles when they are present in environment. Once it will enter the living organism so they behave like living and reproduce by their self. They are not considered as organisms and that’s why they are not included in five kingdom classification. SLO # 3.6.1 : Binomial Nomenclature : Giving Scientific Names of living organisms. Name composed of genus and species names. First part of name should be genus and second part should be species. First part always starts from capital letter and second will be small. Example : Human name is Homo sapiens. SLO # 3.7.1 : Conservation of Biodiversity : To protect or preserve the species of animals those who are going to extinct from the earth. Importance of Conservation : Conservation saves endangered species from extinct which is causing more beauty of nature and also more study about other and ancient animals. It helps us from Acid Rain and Green House Effect by growing more plant’s species which causes lack of these things. It is saving animals and plants species which will help us one day like getting more food, timber and fuel. SLO # 3.7.2 : The impact of human beings on biodiversity is lack of animals and plants species. More animals are dead and their species are extinct from the earth like Baboon and Dodo. The beauty of nature is decreasing day by day and their habitats are destroyed which is causing lack of species. SLO # 3.7.3 : Causes of Deforestation Timber Industrial Resident Fuel Food Causes of Hunting Food Money Ornaments Pleasure Industrial Effects of Deforestation Less of Oxygen CO2 More Pollution Lack of Habitats Effects of Hunting Lack of Species Lack of Ecosystem Lack of Beauty of Nature Lack of Transportation Soil Erosion Flood and Rain Lack of Food SLO # 3.7.4 : Human interference has made endangered the species of animals because they find all their needs from these animals like food and clothes so they do hunting and these are animals who have been endangered by humans like Panda, Tortoise, Kiwi, Gorilla, Parrot, Tiger, Kangaroo, Snakes, Baboon, Indus dolphin, dodo, hippopotamus and Falcon. Made By : Rehman Khosani