Biology I Classification Unit –Chapter 17, 18, 19, 23
advertisement

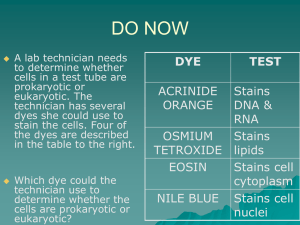
Biology I Classification Unit –Chapter 17, 18, 19, 23-27 Vocabulary (worth 2 grades) Use the biology book to define the following terms: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Taxonomy pg. 518 Taxon pg. 518 Binomial nomenclature pg. 519 Genus pg. 519 Species pg. 298 Cladogram pg. 525 Cladistics pg. 525 Bacteria pg. 534 Archaea pg. 534 Eukarya pg. 534 Scientific Name – consist of genus and species Latin- language scientific names are written in Carolus Linnaeus- developed the classification system we use today Aristotle- developed the first system of classification Dichotomous Key – a way of identifying organisms, there are two or more choices, when finished the name is given Characteristics of Kingdom Protistasome multicellular, some unicellular, cell walls made of cellulose in some, some have chloroplast, ALL are eukaryotic, Some are heterotrophs, some are autotrophs Examples: paramecium, amoeba, slime mold Characteristics of Kingdom Fungi- most multicellular, some unicellular, cell walls made of Chitin, ALL are eukaryotic, ALL are heterotrophs, Examples: mushrooms, mildew, yeast Characteristics of Kingdom Plantae- ALL multicellular, cell walls made of cellulose, have chloroplast, ALL are eukaryotic, ALL are autotrophs Examples: trees, flowers, fruits, vegetables 19. Characteristics of Kingdom Archaebacteria- ALL unicellular, cell walls with NO peptidoglycan, ALL are prokaryotic, Some are heterotrophs, some are autotrophs , are the oldest living organisms on Earth Examples: methanogens, halophiles 20. Characteristics of Kingdom AnimaliaALL multicellular, ALL are eukaryotic, Have no cell wall, ALL are heterotrophs Examples: humans, mammals, birds, fish, reptiles, amphibians 21. Characteristics of Kingdom EubacteriaALL unicellular, cell walls made of peptidoglycan, ALL are prokaryotic, Some are heterotrophs, some are autotrophs , most common bacteria today Examples: E. Coli , Streptococcus 22. Two categories for animals- vertebrates and invertebrates 23. Vertebrates- have backbones 24. Invertebrates- no backbones 25. Asymmetrical- body has no certain shape 26. Radial Symmetry- body arranged around a central point 27. Bilateral Symmetry- body has two equal halves if split lengthwise 28. Chordata- only phylum with vertebrates 29. Organisms in Phylum Porifera-Sponges 30. Organisms in Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms)- Pinworms, Hookworms, Heartworms 31. Organisms in Phylum Arthropoda (Joint Footed)- Spiders, Insects, Crabs, Centipedes, Millipedes 32. Organisms in Phylum Cnidaria- jellyfish, coral, hydra 33. Organisms in Phylum Mollusca- Squid, Octopus, Clams, Snails, Slugs 34. Organisms in Phylum Echinodermata (spiny skin)- starfish, sea urchins, sand dollar 35. Organisms in Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)- tapeworms, planarian, flukes 36. Organisms in Phylum Annelida (segmented worms)- earthworms, leeches 37. Organisms in Phylum Chordata (have notochord)- Fish, reptiles, amphibians, birds, mammals 38. Class Agnatha (Jawless Fish)- have skeleton made of cartilage, have NO jaws, are cold-blooded, Ex. Lampreys, Hagfish 39. Class Chondrichthyes (Cartilaginous Fish)- have skeleton made of cartilage, are cold-blooded, Ex. Sharks, Skates, Rays 40. Class Osteichthyes (Bony Fish)- have skeleton made of bones, are coldblooded, Ex. Perch, Flounder, Bass, Goldfish 41. Class Reptilia (Reptiles)- have dry scaly skin, lay eggs, with protective shells, are cold-blooded, Ex. Snakes, Lizards, Alligators 42. Class Amphibia (Amphibians)- have moist wet skin, live part of life on land and part in water, are cold-blooded, Ex. Frogs, Salamanders, Toads 43. Class Aves( Birds)- Have feathers and beaks , lay eggs with protective shells, are warm-blooded 44. Class Mammalia (Mammals)- Have hair or fur, have lungs, produce milk for their young, are warm-blooded