Weather (Meteorology #2) Study Guide What are scientists who
advertisement

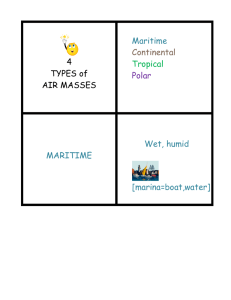
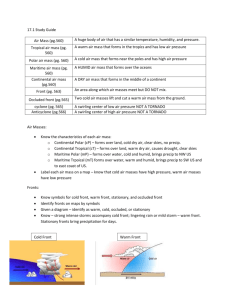
Weather (Meteorology #2) Study Guide What are scientists who study weather called? What is the measure of water vapor in the air? Which air is the “bully” air? Why is cold air the “bully” air? Cold air is more dense so it usually ______. Warm air is less dense so it usually ______. What is a huge body of air with similar temperature, humidity, and pressure? How do scientists classify air masses? What is the term for a humid (wet) air mass? What is the term for a dry air mass? What is the term for a warm air mass? What is the term for a cold air mass? Which type of air mass forms over water? Which type of air mass forms over land? How does the temperature of an air mass determined? Name the North American air masses below: What is formed when two air masses meet and do not mix? What are the four types of fronts? Which type of front is formed when a rapidly moving cold air mass runs into a slow moving warm air mass? Which type of front is formed when a moving warm air mass collides with a slowly moving cold air mass? Which type of front is formed when warm and cold air meet but neither one has enough force to move the other? Which type of front is formed when a warm air mass is caught (cut off) between two cold air masses? Which type of front brings clouds, storms, and steady rain? Which type of front brings severe thunderstorms? Meteorologists humidity Cold air It is more dense than warm air Sinks Rises Air mass Temperature and humidity Maritime Continental Tropical Polar Maritime Continental It takes the temperature of the region it forms over A: Maritime Polar B: Continental Polar C. Maritime Polar D. Maritime Tropical E. Continental Tropical F. Maritime Tropical A front Cold, warm, stationary, & occluded Cold front Warm front Stationary front Occluded front Warm front Cold front Which type of front causes abrupt changes in weather? Which type of front usually causes several days of precipitation? Which type of front uses this symbol? Which type of front uses this symbol? Which type of front uses this symbol? Which type of front uses this symbol? What is a swirling counter clockwise center of low air pressure? What is a swirling clockwise center of high air pressure? What are the lines that join places on a map that have the same air pressure? What are lines joining places on a map that have the same temperature? What is caused by sudden changes in the air pressure in our atmosphere? What happens to air pressure right before a storm? Which type of cloud form thunderstorms? How is thunder formed? What is a rapidly whirling, funnel-shaped cloud that reaches down from a storm cloud to touch Earth’s surface? Which type of cloud develops tornadoes? What is a tropical storm that has winds of 320 kilometers per hour (200 mph) or higher? How are hurricanes formed? Where does a hurricane get its energy? What two things can cause a hurricane to lose its energy? What is the calm part of the hurricane that’s located in the center? What is the condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place? What are the average weather conditions in a particular area over a long period of time? What two main factors determine a regions climate? What factors affect a regions temperature? The closer to the equator the ______a climate will be. The higher the altitude the _______ a climate will be. How does a region’s proximity (how close it is) to water affect its climate? Why is our Earth heated unequally? Which part of our Earth receives the most direct sunlight? Which part of our Earth receives the least amount of direct sunlight? Which climate zone do we live in? Cold front Stationary front Stationary front Occluded front Warm front Cold front Cyclone Anticyclone Isobars Isotherms (remember “therm” means heat) Storms It drops (decreases quickly) Cumulonimbus It is the explosion heard when rapidly heated air suddenly expands A tornado Cumulonimbus Hurricane A hurricane begins over warm water as a low-pressure area From warm, humid (wet) air Moving overland or moving over cold water The eye Weather Climate Temperature and precipitation Latitude, altitude, distance from water, & ocean currents Warmer Cooler Because water holds its temperature a region closer to water will have a milder climate than regions inland Because the Earth is tilted The equator; tropical zone The poles; polar zones The temperate zone