File
advertisement

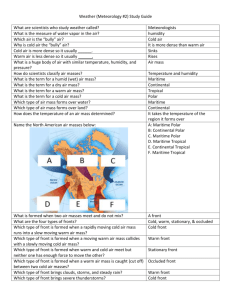
Air mass -Large body of air where temperature and moisture are similar throughout the mass -changes in weather are caused by movement and interaction of air masses Characteristics of air masses 1- moisture 2-temperature Source region – an area over which an air mass forms Source regions are identified by 2 letters EX: Maritime polar mP 1st letter represents moisture level 2nd letter represents temperature Cold Source regions (3) that affect weather in the continental US 1 Continental Polar (cP) Forms over N Canada Winter-brings extremely cold air to U.S. Summer-brings cool dry air to U.S. 2 Maritime Polar (mP) water (wet) & cold Forms over N Atlantic Ocean Winter- brings rain and snow to Pacific coast area (CA) Summer-brings cool, frosty air to Pacific Coast area 3 Maritime Polar (mP) Forms over N Pacific Ocean Winter-cool and cloudy to N England area (MA) summer-cool and foggy to N England area WARM Source Regions(4) that affect weather in the continental US 1 Maritime Tropical (mT) wet and warm Source region- warm areas of the Pacific Ocean Summer: brings hot, humid weather with hurricanes and thunderstorms to the West coast and Midwest 2 Maritime Tropical (mT) wet and warm Source region- warms areas of the Atlantic Ocean Summer: brings hot, humid weather with hurricanes and thunderstorms to the East coast and Midwest 3 Maritime Tropical (mT) wet and warm Source region-over Gulf of Mexico Weather to the East coast and Midwest: Summer: hot, humid weather with hurricanes and thunderstorms Winter: mild, often cloudy 4 Continental Tropical (cT) dry and warm Source region: deserts of N Mexico and SW U.S. Summers are clear, dry and hot Fronts are where two types of air masses meet Four kinds of fronts 1-cold fronts- cold air mass moves under warm air mass thunderstorms, heavy rain or snow 2-warm fronts-warm air mass moves over cold air mass drizzly rain followed by clear and warm weather 3-occluded fronts-warm air mass gets caught b/t 2 cold air masses cool temps and large amounts of rain and snow 4-stationary fronts-cold air mass meets a warm air mass brings many days of cloudy, wet weather Cyclones are areas with lower pressure than the areas around them -air masses converge and rise -rising air from the center of a cyclone cools and forms clouds causing stormy weather Anticyclones are areas with higher pressure than the areas around them -air masses diverge and sink -sinking air of an anticyclone gets warmer and absorbs moisture bringing dry, clear weather