Zoology Unit Exam 1: What to Study PowerPoint
advertisement

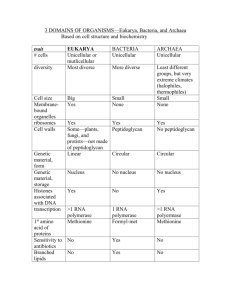
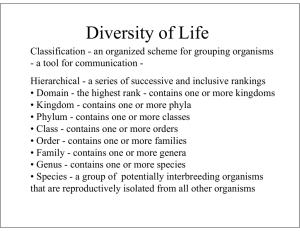
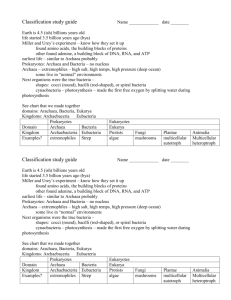
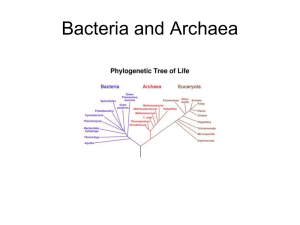
Zoology Unit Exam 1: What to Study PowerPoint fill-in-the-blank notes (…begins with Definitions) Understand a logical order for the scientific method: 1) Observation; 2) ask a Scientific Question; 3) propose a Scientific Hypothesis; 4) perform an Investigation: Experiment or Collection of Data; 5) Analyze the Data with Tables, Graphs, or Statistics; 6) make Conclusions including accept or reject Hypothesis Understand and be able to interpret graphs/figures and tables Biotic (living) and Abiotic (non-living) components of Ecosystems (remember your drawing of an ecosystem?) Darwin’s voyage on the ship H.M.S. Beagle led him to propose a revolutionary hypothesis about ….. (p. 369; Key Concept ) The way life changes over time = Evolution Darwin’s hypothesis about how life changes over time is now called….. (p.369) The Theory of Evolution On the Galapagos Islands, Darwin observed that the characteristics of many animals and plants……… (p. 372; Key Concept) Varied greatly amongst the Islands How did the birds (finches) differ among the islands of the Galapagos? (p. 372) Shape of their beaks Based on what Darwin learned about certain birds on the Galapagos Islands, hypothesize what the differences can tell you about the eating habits of these finches. (p. 372) They eat different things (have different diets) since beaks are different. What is an adaptation? (p. 380) Any inherited characteristic that increases an organisms chance of survival Over time, what is the result of natural selection? (p.381 Key Concept) Changes in the inherited characteristics of a population, possibly increasing the fitness of a species in its environment There are currently ~1.1 million animal species that have been described by zoologists; How many overall species (includes plants , fungi, bacteria) have been named? (p.447) ~1.5 million How many overall species are estimated to be on the earth? (p.447) 2 to 100 million How are living things organized for study? (p.447 Key Concept) With a classification system, grouping them in a logical manner Linnaeus developed binomial nomenclature; what is it? (p.448 Key) two-part scientific name Do Ursus arctos (grizzly bear) and Ursus maritimus (polar bear) belong to the same species? Yes or No To the same genus? Yes or No (p.448 & Figure on p.450) What are the three domains of life? (p.458 key concept) Bacteria (such as on or in your body), Archaea (bacteria-like organisms found in extremely harsh environments such as salt lakes or hot springs), Eukarya (all organisms with a nucleus = eukaryotes; protists such as Amoeba or Paramecium, fungi such as a mushroom, plants, animals including you!) What are the six kingdoms of life as they are now identified? (p.458 Key Concept) Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia Autotrophs make their own food (like a plant); Heterotrophs must obtain theirs (like animals) Eukaryotes have a nucleus (= Domain Eukarya); Prokaryotes do NOT have a nucleus (= Domains Archaea and Archaebacteria) Multicellular or Unicellular heterotrophs whose cell walls contain chitin: Domain Eukarya; Kingdom Fungi (e.g. mushroom) Strictly prokaryotes (= no nucleus) whose cell walls contain peptidoglycan; bacteria: Domain Bacteria; Kingdom Eubacteria (e.g. body bacteria) Strictly multicellular, eukaryotic autotrophs whose cell walls contain cellulose: Domain Eukarya; Kingdom Plantae (e.g. trees; flowers; grasses) Strictly prokaryotes (= no nucleus) whose cells walls lack peptidoglycan; found in harsh environments; bacteria-like organisms: Domain Archaea; Kingdom Archaebacteria (e.g. prokaryotes that are bacteria-like found in salt lakes or hot springs) Strictly multicellular eukaryotes without cell walls or chloroplasts: Domain Eukarya; Kingdom Animalia (e.g. deer, humans, earthworm, sponges, crayfish)