Respiratory_Infections_Path_1
advertisement
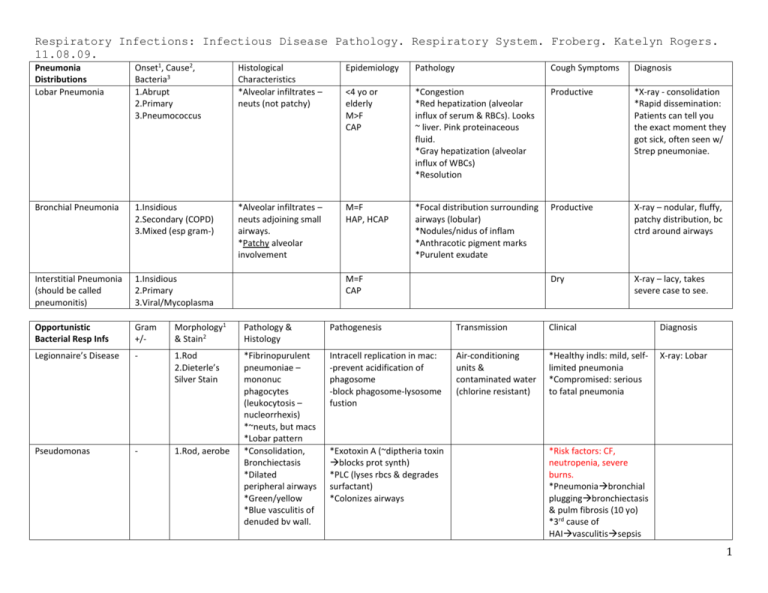
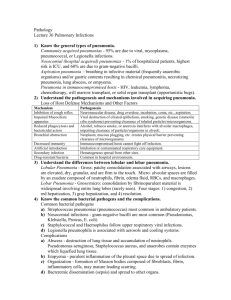
Respiratory Infections: Infectious Disease Pathology. Respiratory System. Froberg. Katelyn Rogers. 11.08.09. Pneumonia Distributions Lobar Pneumonia Onset1, Cause2, Bacteria3 1.Abrupt 2.Primary 3.Pneumococcus Histological Characteristics *Alveolar infiltrates – neuts (not patchy) Epidemiology Pathology Cough Symptoms Diagnosis <4 yo or elderly M>F CAP *Congestion *Red hepatization (alveolar influx of serum & RBCs). Looks ~ liver. Pink proteinaceous fluid. *Gray hepatization (alveolar influx of WBCs) *Resolution Productive *X-ray - consolidation *Rapid dissemination: Patients can tell you the exact moment they got sick, often seen w/ Strep pneumoniae. Bronchial Pneumonia 1.Insidious 2.Secondary (COPD) 3.Mixed (esp gram-) *Alveolar infiltrates – neuts adjoining small airways. *Patchy alveolar involvement M=F HAP, HCAP *Focal distribution surrounding airways (lobular) *Nodules/nidus of inflam *Anthracotic pigment marks *Purulent exudate Productive X-ray – nodular, fluffy, patchy distribution, bc ctrd around airways Interstitial Pneumonia (should be called pneumonitis) 1.Insidious 2.Primary 3.Viral/Mycoplasma Dry X-ray – lacy, takes severe case to see. Opportunistic Bacterial Resp Infs Gram +/- Morphology1 & Stain2 Pathology & Histology Pathogenesis Transmission Clinical Diagnosis Legionnaire’s Disease - 1.Rod 2.Dieterle’s Silver Stain Intracell replication in mac: -prevent acidification of phagosome -block phagosome-lysosome fustion Air-conditioning units & contaminated water (chlorine resistant) *Healthy indls: mild, selflimited pneumonia *Compromised: serious to fatal pneumonia X-ray: Lobar Pseudomonas - 1.Rod, aerobe *Fibrinopurulent pneumoniae – mononuc phagocytes (leukocytosis – nucleorrhexis) *~neuts, but macs *Lobar pattern *Consolidation, Bronchiectasis *Dilated peripheral airways *Green/yellow *Blue vasculitis of denuded bv wall. M=F CAP *Exotoxin A (~diptheria toxin blocks prot synth) *PLC (lyses rbcs & degrades surfactant) *Colonizes airways *Risk factors: CF, neutropenia, severe burns. *Pneumoniabronchial pluggingbronchiectasis & pulm fibrosis (10 yo) *3rd cause of HAIvasculitissepsis 1 *Leading cause of HAP Gram +/- Morphology Pathology & Histology Pathogenesis Clinical Rod Edema, orgs grown on surface. WBC = lymphocytosis Attaches to resp mucosal cilia & kills cell by cytotoxin (blocks signal transduction) Corynebacterium Diptheriae (Diptheria) + Rod Hemophilus Influenzae (“Bully of the Pharynx”) - Rod *Purulent *Toxin myocardial fiber necrosis & peripheral nerve damage *Diptheritic memb: fibrin + dead cells + bact liver to necrotic *Red cells = dead *Narrowing of glottis *Mucosal pustules (bact + neut infiltrate) & small abscesses. Orgs grow on surf of colonized larynx & trachea phage coded exotoxin kills mucosa. Purulent resp = “pseudomemb” (dead mucosa + PMNs + fibrin) detachment aspirationdeath. NO INVASION. Encapsulated (5%-type b) form evades phagoctyosis causing illnesses. Erosive, acute laryngotracheitis, edema “whoop” Leathery pseudomemb covers pharynx, larynx, & trachea is fatal. Bordetalla Pertussis (Whooping Cough) Virulence Factors: *Polysaccharide capsule *Capsule is a polymer of polyribitol phospate *Produces IgA protease *Endotoxin (LPS) Mycoplasma & viruses (Atypical Pneumonia) fungi *Interstitial pneumonitis: mononuclear cells (lymphs & macs) confined to interstitium *Alveolar walls widened & edematous, no consolidation unless secondary bact infection M. pneumoniae most common -bacteria minus cell wall Viruses have to be w/in the cell to cause dx. Sudden onset, sore throat, hoarseness, stridor. Capsulated forms: *Pharyngolaryngitis & epiglottis (swollen,red); edema resp death *Meningitis – previously most common cause in <5yo. *Pneumonia *Bacteremia (really all are emergencies) Uncapsulated forms: *Local Pharyngitis *Otitis media Treatment1 & Prevention2 1.Antibiotics 2.DPT vaccine early 2. DPT vaccine 1.Antibiotics 2.PRPconjugated protein vaccine decd meningitis. (Does not prevent infection by encapsulated forms) Esp teens, fever, nonproductive cough, cold agglutinins (IgM) 2 3