Current Acid-test Debt to Action Ratio Ratio Equity Ratio
advertisement

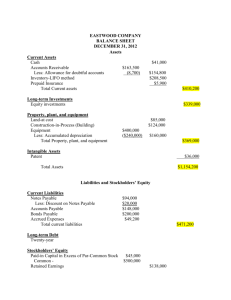
Solutions Guide: This is meant as a solutions guide. Please try reworking the questions and reword the answers (especially essay type parts) so as to guarantee that your answer is an original. Do not submit as your own. Week One Assignment Intermediate Accounting 1 Calculating ratios: solve the unknown The current asset section of the Excalibur Tire Company’s balance sheet consists of cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, and inventories. The December 31, 2011 balance sheet revealed the following: Inventories 840,000 Total Assets 2,800,000 Current ratio 2.25 Acid –test ratio 1.2 Debt to equity 1.8 Required: Determine the following 2011 balance sheet items: 1. Current assets 2. Shareholder’s equity 3. Noncurrent assets 4. Long-term liabilities 1. Acid-test ratio = Quick assets ÷ Current liabilities = Quick assets = Current assets - Inventories Quick assets = Current assets - $840,000 1.20 Current assets ÷ Current liabilities = Current assets - $840,000 ÷ Current liabilities = $840,000 ÷ Current liabilities = Current liabilities = $800,000 Current assets ÷ $800,000 = 2.25 Current assets = $1,800,000 2.25 1.20 1.05 2. Debt to equity ratio = Total liabilities ÷ Shareholders’ equity = 1.8 Total liabilities + Shareholders' equity = Total assets Total liabilities + Shareholders' equity = $2,800,000 Let x equal shareholders' equity 1.8 x + x = $2,800,000 x = $1,000,000 = Shareholders' equity 3. Noncurrent assets = Total assets - Current assets Noncurrent assets = $2,800,000 – 1,800,000 = $1,000,000 4. Long-term liabilities = Total assets - Current liabilities - Shareholders' equity Long-term liabilities = $2,800,000 - 800,000 - 1,000,000 = $1,000,000 2 Effect of management decisions on ratios Most decisions made by management impact the ratios analysts use to evaluate performance. Indicate (by letter) whether each of the actions listed below will immediately increase (I), decrease (D), or have no effect (N) on the ratios shown. Assume each ratio is less than 1.0 before the action is taken. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Current Action Ratio Issuance of long-term bonds I Issuance of short-term notes I Payment of accounts payable D Purchase of inventory on account I Purchase of inventory for cash N Purchase of equipment with a 4-year note N Retirement of bonds D Sale of common stock I Write-off of obsolete inventory D Purchase of short-term investment for cash N Decision to refinance on a long-term basis some currently maturing debt I Acid-test Debt to Ratio Equity Ratio I I I I D D D I D N N I D D I D N I N N I 3 Balance Sheet Errors You recently joined the internal auditing department of Marcus Clothing Corporation. As one of your firs assignments you are examining a balance sheet prepared by a staff account. In the course of your examination you uncover the following information pertaining to the balance sheet: N 1. The company rents it facilities. The land that appears in the statement is being held for future sale. 2. The note receivable is due in 2013. The balance of 53,000 includes 3,000 of accrued interest. The next interest payment is due in July 2012. 3. The note payable is due in installments of 20,000 per year. Interest on both the notes and bonds is payable annually. 4. The company’s investments consist of marketable equity securities of other corporations. Management does not intend to liquidate any investments in the coming year. Required: Identify and explain the deficiencies in the statement prepared by the company’s accountant. Include in your answer items that require additional disclosure, either on the face of the statement or in a note. DEFICIENCIES: 1. Accounts receivable - if material, the allowance for uncollectible accounts should be disclosed. 2. Note receivable - only the interest receivable of $3,000 should be classified as a current asset. The $50,000 note receivable should be classified in the noncurrent Investments category. 3. Inventories - the method used to cost inventory should be disclosed in a note. 4. Investments - should be classified in the noncurrent Investments category. Also, disclosures include information about the types of investments and the accounting method used to value the investments. 5. Prepaid expenses - in the absence of information to the contrary, should be classified as a current asset. 6. Land - should be classified in the noncurrent Investments category. 7. Equipment, net - should be classified in the Property, plant, and equipment category. Original cost should be disclosed along with the accumulated depreciation to arrive at the net amount. Also, the method used to compute depreciation should be disclosed in a note. 8. Patent - should be classified in the Intangible assets category of noncurrent assets. 9. Note payable - $20,000, the next installment, should be classified as a current liability as current maturities of long-term debt. Also, note disclosure is required for the note and bonds payable that provides information such as payment terms, interest rates, and collateral pledged as security for the debt. 10. Interest payable - should be classified as a current liability. 11. Common stock - the par value, if any, and the number of shares authorized, issued and outstanding should be disclosed.