Financial Management PowerPoint Pt. 2
advertisement

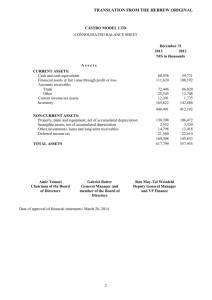
Chapter 17 Managing Business Finances Section 17.2 Accounting Read to Learn Explain the purpose of accounting. Describe how property rights are measured. Define the three components of the accounting equation. Describe the three main financial statements used by businesses. The Main Idea Accounting provides financial information about an organization. It also helps guide business decisions regarding operations and finances. Balance sheets, income statements, and statements of cash flows show the financial position of a business. Key Concepts Accounting for Business Property Ownership and Control Financial Statements Key Terms the systematic process of recording accounting and reporting the financial position of a person or an organization generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) the set of accounting rules used by accountants to prepare reports Key Term anything of value that is owned or property controlled assets property and other items of value owned by a business Key Term current assets assets that are either used up or converted to cash during the normal cycle of the business accounts receivable the total amount of money owed to a business Key Term fixed assets items of value that will be held for more than one year equity the present value of an asset less all claims against it Key Term creditors’ claims to the assets of a liabilities business accounts the short-term liabilities that a business payable owes to creditors Key Term owner’s equity an owner’s claim to the assets of the business a rule that states that assets must accounting always equal the sum of liabilities and equation owner’s equity Key Term documents that summarize the financial changes resulting from business statements transactions that occur during an accounting period income statement a report of the revenue, expenses, and net income or net loss of an accounting period Key Term a report of the balances in all assets, balance liabilities, and owner’s equity accounts at sheet the end of an accounting period cash flows the money that is available to a business at any given time Key Term statement of cash flows a financial report that shows incoming and outgoing money during an accounting period Accounting for Business Many companies hire accounting firms to manage or audit their financial records. accounting the systematic process of recording and reporting the financial position of a person or an organization Accounting for Business An accountant maintains and reviews business records. An audit is a review of accounting records and procedures. Accounting Software There are software categories for all levels of accounting, from home use to high-end corporate use. Accounting for Business Accounting is often called the “language of business.” Everyone involved in a business should understand the basics of accounting. Questionable Accounting Some companies have gotten into legal trouble for committing accounting fraud. Fraud is the crime of intentionally deceiving others for financial gain or some other benefit. Rules for Accountants Each company sets up an accounting system according to its specific needs, but all businesses follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) the set of accounting rules used by accountants to prepare reports Property Ownership and Control The right to own property is basic to a free enterprise system. Accounting provides financial information about property and rights to it. property anything of value that is owned or controlled Property Ownership and Control In accounting, property and financial claims are measured in dollar amounts. Dollar amounts measure the cost of property and the property rights, or financial claims to the property. Financial Claims in Accounting Land and equipment are examples of assets. assets property and other items of value owned by a business Financial Claims in Accounting Current assets include cash, supplies, merchandise, and accounts receivable. current assets assets that are either used up or converted to cash during the normal cycle of the business accounts receivable the total amount of money owed to a business Financial Claims in Accounting Equipment and buildings are examples of fixed assets. fixed assets items of value that will be held for more than one year Financial Claims in Accounting The accounting term for the financial claims to all assets is equity. equity the present value of an asset less all claims against it Financial Claims in Accounting When a person or business buys property and agrees to pay for it later, they are buying on credit. The business or person selling the property is called the creditor. Financial Claims in Accounting Liabilities are measured by the amount of money a business owes its creditors. liabilities creditors’ claims to the assets of a business Financial Claims in Accounting Owner’s equity is also referred to as the owner’s capital. owner’s equity an owner’s claim to the assets of a business The Accounting Equation The accounting equation ensures that all accounting records will be correct. accounting equation a rule that states that assets must always equal the sum of liabilities and owner’s equity Graphic Organizer The Accounting Equation = Assets Liabilities + Owner’s Equity + Owner’s Equity: $60,000 Example Company Assets: $100,000 = Liabilities: $40,000 The owner’s rights to the assets that the owner possesses. Financial Statements The accounting system is designed to generate financial statements. financial statements documents that summarize the changes resulting from business transactions that occur during an accounting period Financial Statements Financial statements provide information that business owners use to make financial decisions. Financial Statements Stockholders, employees, banks, and investment companies use financial statements to learn about the financial conditions of a business. Corporations must release their financial statements to the public. Income Statements The income statement is sometimes called a profit and loss statement. income statement a report of the revenue, expenses, and net income or net loss over an accounting period Income Statements Total revenue is greater than total expenses Net income $ Total revenue is less than total expenses Net loss $ Balance Sheet A balance sheet is like a photograph of a business’s finances at a specific moment. balance sheet a report of the balances in all assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity accounts at the end of an accounting period Balance Sheet The balance sheet applies the accounting equation. When added up, the two sides of the equation are equal, or in balance. Statement of Cash Flows Cash flows are not indicated in the income statement or the balance sheet. cash flows the money that is available to a business at any given time Statement of Cash Flows The statement of cash flows helps managers ensure that the business does not run out of money. statement of cash flows a financial report that shows incoming and outgoing money during an accounting period Statement of Cash Flows Lenders and investors expect business loan applicants to be able to show a consistently positive cash flow. Computerized Accounting Most companies use computer programs to simplify their accounting procedures because they are efficient at organizing and analyzing data. Graphic Organizer In a spreadsheet, rows are identified by numbers. Graphic Organizer In a spreadsheet, columns are identified by letters. Graphic Organizer Cells are the small boxes in a spreadsheet. Graphic Organizer As you create a spreadsheet, you enter numbers, labels, and formulas into cells. Figure 17.1 Income Statement Using Peachtree Software Figure 17.2 Balance Sheet Using QuickBooks® Software 1. How does accounting help a business? Accounting keeps track of money and shows how a business is doing. 2. Discuss property ownership and control. How are they related to the accounting equation? The person who owns property has a financial claim to it. The accounting equation indicates the amounts of financial claims to property. 3. What are the three main financial statements used in business? balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows End of Chapter 17 Managing Business Finances Section 17.2 Accounting