Midterm Study Guide KEY p.2
advertisement

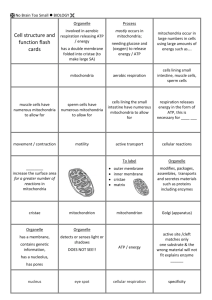
Midterm Study Guide KEY p. 2 Enzymes Vocabulary: Catalyst – a molecule that starts a reaction Substrate – molecule that reacts with an enzyme Active site – area on an enzyme where reactions take place Activation energy – energy necessary in order for a reaction to occur Induced fit model – perfect fit between a substrate and its enzyme (like a lock and key) Denaturation – deactivation of an enzyme due to drastic change in temperature or pH Questions 1. What is the function of an enzyme? Enzymes can speed up a reaction. Enzymes can start a reaction (catalyze). Enzymes can lower the activation energy. 2. In the picture below, which reaction most likely involves an enzyme? Reaction 3 Macromolecules Macromolecule Monomer/Polymer Elements/Components involved Examples Protein Amino Acid/Polypeptide C, H, O, N / Carboxyl group, Amino group, R group Meats Lipids Fatty acids/ Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Waxes, Steroids C, H / Glycerol, Fatty acids, Phosphate group (phospholipids) Oils Carbohydrates Monosaccharide/ Polysaccharide C, H, O / Sugars Bread Nucleic Acids Nucleotide/DNA or RNA C, H, O, N, P / Sugar, Phosphate group, Nitrogenous base DNA Questions 1. What reagents are used to test for each of the macromolecules? a. Lipids Paper Positive result: Transparent, Negative result: Opaque b. Carbohydrates Benedict’s solution Positive result: Green/Orange, Negative result: Blue c. Proteins Biuret Positive result: Purple, Negative result: Blue d. Starch Iodine Positive result: Black, Negative result: Red/orange The Cell Vocabulary identify the structure and function of the following organelles Mitochondria – organelle that creates energy Vacuole – organelle that stores water, wastes, and salts Plasma membrane – organelle that surrounds cell and regulates what can enter and leave Nucleus – organelle that holds genetic information Cell wall – ridged organelle that surrounds plasma membrane and provides strength and structure to plant and bacteria cells Golgi apparatus – organelle that packages and ships molecules in the cell Ribosomes – organelle that makes proteins Nuclear envelope – membrane that surround the nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum – organelle that aids in transport of molecules with ribosomes attached to its membrane Smooth endoplasmic reticulum – organelle that aids in transport of molecules Chloroplast – organelle where photosynthesis takes place (plant cells only) Chromosomes – condensed form of DNA Questions 1. List the scientists involved with early cell discoveries and identify their contribution. Robert Hooke Saw cork cells under microscope Anton van Leeuwenhoek Made first light microscope and saw first cells 2. How is surface area relevant to cell size? Cell size is limited by its surface area. As cell size decreases, surface area increases. 3. What are the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Prokaryotes Smaller Bacteria/Archaea No membrane bound nucleus (nucleoid) Eukaryotes Larger Plants/Animals Membrane bound nucleus 4. What are the differences between plant and animal cells? Plant Nucleus is off centered Chloroplasts Cell wall Central vacuole Animal Nucleus in center Centrioles Lysosomes