Supplementary Section - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement

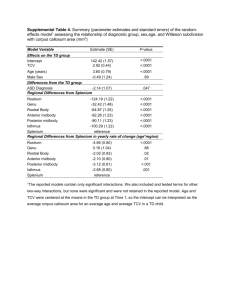
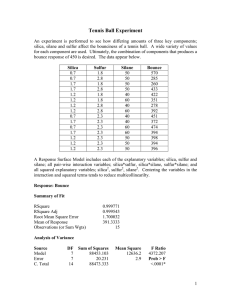
McKee and Gilbreath, 2015. CONCENTRATIONS AND LOADS OF SUSPENDED SEDIMENT AND TRACE ELEMENT POLLUTANTS IN A SMALL SEMI-ARID URBAN TRIBUTARY, SAN FRANCISCO BAY, CALIFORNIA Lester J. McKeea* and Alicia N. Gilbreatha a San Francisco Estuary Institute, 4911 Central Avenue, Richmond CA 94804, USA * Corresponding author: lester@sfei.org; phone 510-746-7363; Fax 510-746-7300 Supplementary Section Figure S1. Relationships between turbidity and trace element concentrations and suspended sediment concentrations (SSC) illustrating correlation lines (or the lack thereof) and the 95% confidence interval. Note the outliners represented by the triangle symbols were not used in the regression equations used to loads estimation. The outliers were from the same four samples for nickel and chromium. A thorough quality check did not reveal any reason to reject these data. 1 of 3 McKee and Gilbreath, 2015. Figure S2. Relationships between flow and trace element concentrations and suspended sediment concentrations (SSC) illustrating the lack of a strong correlation in most cases and the 95% confidence interval. 2 of 3 McKee and Gilbreath, 2015. Table S1. The coefficient of determination and p-values for linear regression relationships between analytes and flow and turbidity. This illustrates the value of using turbidity as a surrogate measurement for most trace elements that are dominantly transported in particulate phase. It also demonstrates that flow, in most cases, is a poor predictor of concentration. The use of the turbidity surrogate method addresses the key challenge of collecting representative samples during short lived high flow conditions in arid-climate systems. The results demonstrate the use of a surrogate measurement that can easily and reliably be logged at short time intervals and used to estimate concentrations during critical peak flows. These estimate couple with flow measurements at the same time interval can be used to compute reliable loads estimates that can be summed to any other time interval desired (hourly, storm, weekly, monthly, or annual). Flow Analyte Turbidity p-value r² Aluminum r² 0.42 0.0016 0.94 p-value <0.0001 Cadmium 0.45 0.0009 0.86 <0.0001 Chromium 0.63 0.0001 0.87 <0.0001 Copper 0.02 0.3939 0.86 <0.0001 Iron 0.03 0.5826 0.97 <0.0001 Lead 0.53 0.0002 0.87 <0.0001 Nickel 0.44 0.0039 0.59 <0.0001 Silver 0.37 0.0002 0.74 <0.0001 Zinc 0.46 0.0007 0.87 <0.0001 HgT 0.05 0.75 <0.0001 SSC 0.08 0.0362 <0.0001 0.84 <0.0001 3 of 3