PULSELESS ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY - SIM-one
advertisement

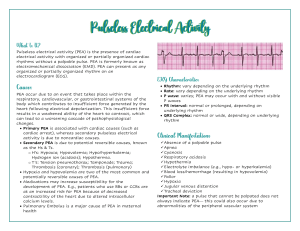
PULSELESS ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY I. Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) II. Learning Objectives: a) Primary 1. Describe management of pulseless electrical activity cardiac arrest 2. Perform chest compressions and manual ventilation as per ACLS guidelines 3. Administer epinephrine according to ACLS guidelines 4. Recall the differential diagnosis of PEA and systematically eliminate possible causes 5. Describe some key components of clinical teamwork and identify applications in their practice b) Secondary 1. Review contents of emergency ‘crash’ cart 2. Identify methods of improvement of non- technical skills/behavioral skills III. Case A. Scenario Background Given to Participants-a patient chart, consisting of the usual documents as per individual institutional protocol will be available to the participants. The `patient` will be available for a preoperative interview by perioperative team members. 1. Chief Complaint: a) Right upper quadrant pain. Gallstones discovered by U/S (General surgery) b) Right lower quadrant pain for 6-8 weeks. U/S shows 4 cm ovarian cyst (Gynecology) c) Presents for left knee ACL, following injury (Orthopedic) 2. Past Medical History: Patient is a cooperative middle aged woman who gives a history of hypertension treated with Altace and a recent diagnosis of NIDDM for which she takes Metformin 500 mg bid. She denies any secondary issues related to either her hypertension or her diabetes. She is a 35 year pack a day smoker. Her exercise tolerance is limited by knee arthritis; she was seen by an anesthetist in the PAC and a consult note is on the chart. She presents for a laparoscopic cholecystecomy/ovarian cystectomy/knee arthroscopy. BIRTHDATE: May 16, 1959 3. Medications and Allergies: Altace 2.5 mg OD, Metformin 500 mg bid. No allergies. 4. Family/social history: Father died at age 62 from myocardial infarction. Mother died age 75 of stroke. B. Scenario Conditions Initially 1. History patient gives: As above 2. Patients initial exam: Vital Signs are stable. BP 150/90, HR 72 3. Patients physiology: 55 year old woman with increased risk for perioperative cardiac event C. Scenario Branch Points 1. Changes in patient’s condition: Patient’s condition stable before and after induction of anesthesia and continues as such until about 5 mins after surgeon begins cognitive load, when the ↓↓ST segments, (↓BP, ↓O2, ↓CO2). Anesthesiologist will manage this for 1-2 mins. Loss of pulse, electrical activity persists. Allow 5-7 mins for mgt of PEA; if no action towards resuscitation (ie PEA not recognized) bring VS back to normal. 2. Responses to treatment: All changes in VS will improve with the correct treatment interventions. If incorrect or no interventions, VS should return to normal after 5-7 mins. 3. Usually there are several directions scenario can be taken: If incorrect, slow or no interventions, all VS should deteriorate but not to the point of cardiac arrest. All VS should return to normal at 5-7 mins despite treatment.