GCSE Physical Education
advertisement

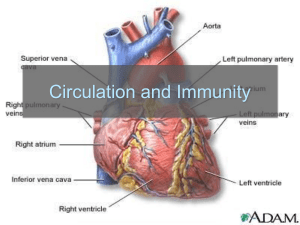
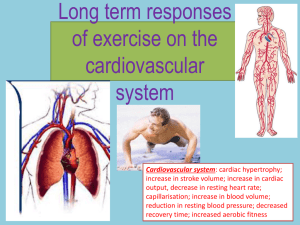
GCSE Physical Education The Cardiovascular system (2) Answer the questions below 1 2 6 3 5 4 7 Identify no’s 1-7 on the Heart diagram Identify the immediate effects of exercise on the CV system. Extension Question Explain how the ‘Double Pump’ system works. What are the immediate effects of exercise on the heart? The heart beats faster and stronger to supply more oxygen to the muscles. This is caused by adrenaline, a hormone released during exercise. Body temperature- muscles generate heat which causes the body temperature to rise. Sweat- To cool down the body produces sweat. ENERGY is needed to make the sweat evaporate and this causes the temperature to fall. Lactic acid- when your muscles demand more oxygen than can be supplied lactic acid builds up causing muscle fatigue. = By the end of this lesson you should… Be able to Define the following terms: Heart Rate (HR) Stroke Volume (SV) Cardiac Output (Q) Identify the long term effects & benefits of exercise on the Cardiovascular system. Watch the video How long is the CV system? What health conditions relating to the CV system are mentioned? High cholesterol Cholesterol is a fatty substance carried in the blood by lipoproteins. Lipoproteins come in 2 forms: High Density (HDL) Low Density (LDL) HDL contains more protein than fat & is referred to ‘good cholesterol’ because it carries cholesterol away from the arteries to the liver which removes it. LDL consists of mainly fat. It is the major cause of cholesterol in the blood, & it can lead to a build up of plaque which can restrict blood flow in the arteries. Blockages result in an increase in blood pressure Heart rate (HR) Heart Rate The number of times the heart beats per minute (bpm) Can vary considerably from person to person, Average resting HR = 72 bpm Elite athlete e.g Lance Armstrong, Steve Redgrave, Paula Radcliffe can have significantly lower resting HR’s. Max Heart Rate 220 - age Stroke Volume (SV) The volume of blood ejected from the heart in one heart beat. At rest: approx 80ml During exercise: up to 130ml Cardiac Output (Q) The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one minute Cardiac Output = Heart Rate x Stroke Volume Q HR SV Immediate effects of Exercise on the Heart Muscles need oxygen to work. During exercise the demand for Oxygen is increased. Therefore; the cardiac output needs to be increased. This is achieved by an increase in Heart Rate and Strove Volume. Task In small groups (2-3) Identify as many long term effects of exercise on the CV system as you can. With increasing fitness the following occur: The heart pumps more blood every beat. After Before Beats per minute 160 140 100 Recovery rate = 5 mins 60 0 Beats per minute Time (mins) 160 140 Recovery rate = 2 mins 100 60 0 Time (mins) Long term effects of exercise Endurance training, commonly known as aerobic/cardiovascular training, helps strengthen the heart. With training the general size of the heart gets bigger, the walls become thicker and stronger. 20 mins + @ 60-80% of max HR Myocardial hypertrophy. Therefore: The SV increases Resting HR decreases (bradycardia) Can work for longer at higher intensities. By the end of this lesson you should… Be able to Define the following terms: Heart Rate (HR) Stroke Volume (SV) Cardiac Output (Q) Identify the long term effects & benefits of exercise on the Cardiovascular system. Homework Research the effect of lifestyle on the CV system. You will need to be able to explain: The need for rest & recovery time The impact of diet on the CV system, in particular how it can effect blood pressure and cholesterol The effects of recreational drugs