Signal Addition
advertisement

Signal Operations
LAB# 05
Course Title: Signal and System
Course Code: EEE223
Instructor Name:
Student Name:
Registration No:
Class:
Semester:
Due Date:
COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
Attock, Pakistan
Spring, 2013
Prepared by: Engr.Muhammad Bilal Khan
Signal Addition:
If sequences are of unequal lengths, or if the sample positions are different for equal-length sequences,
then we cannot directly use the operator +. We have to first augment x1 (n) and x2 (n) so that they have
the same position vector n.
Following function sigadd is used to accomplish this:
function [y,n] = sigadd(x1,n1,x2,n2)
n = min(min(n1) ,min(n2)) :max(max(n1) ,max(n2)) ;
y1 = zeros (1,length(n)); y2=y1;
y1 (find((n>=min(n1))&(n<=max(n1))==1))=x1;
y2 (find((n>=min(n2))&(n<=max(n2))==1))=x2;
y = y1+y2;
Note: Signal Multiplication can be carried out in the similar way using “.*” operator.
4.2 Signal Shifting:
In this operation each sample of x(n) is shifted by an amount k to obtain a shifted sequence y(n).
y(n) = x(n-k)
This operation has no effect on x but vector n is changed by adding shifted amount to each element.
function [y,n] = sigshift(x,m,n0)
n = m+n0; y=x;
Prepare by: Engr. Muhammad Bilal Khan
Page 2
4.3 Signal Folding
In this operation each sample of x(n) is flipped around n = 0 to obtain a folded sequence y(n).
y(n) = {x(-n)}
This operation can be carried out by the following function
function [y,n] = sigfold(x,n)
y = fliplr(x); n = - fliplr(n);
4.4 Even-Odd synthesis
A real-valued sequence x(n) is called even (symmetric) if
xe (-n) = xe (n)
Similarly, a real-valued sequence x(n) is called odd (antisymmetric) if
xo(-n) = -xo(n)
Then any arbitrary real-valued sequence z(n) can be decomposed into its even and odd components
x(n) = xe(n) + xo(n)
where the even and odd parts are given by
Prepare by: Engr. Muhammad Bilal Khan
Page 3
Exersise#5
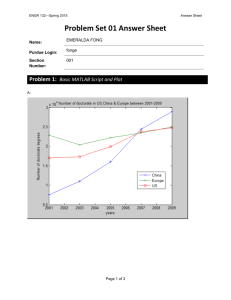
Task(1): Let x1={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, n1= {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5},
x2 ={-1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6} ,n2 = {-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0}
Determine and plot the following sequences
y = x1+x2
z = x1 * x2
Task(2): Let x = {1,2,2,4,4,4,2,2,1}
Generate and plot the following sequence
y(n) = x(n+3)
z(n) = x(n-3)
Task(3): Let x(n) = {1,-1,2,-2,3,-3}
Generate and plot the following sequence
y(n) = x(-n)
Task(4): Let x(n) = {0,0,0,1,2,3,4} and -3 ≤ n ≤ 3
Determine and plot its even and odd part
Task(5): Let x(n) = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,6,5,4,3,2,1}. Determine and plot the following sequence:
Prepare by: Engr. Muhammad Bilal Khan
Page 4