Exam 1 Study Guide – General Concepts
advertisement

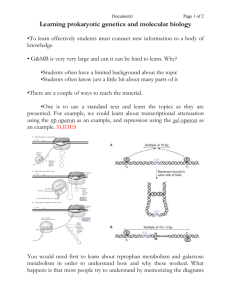
BIO 184 Laboratory CSU, Sacramento Fall 2008 EXAM 2 STUDY GUIDE – GENERAL CONCEPTS Single-Gene Mutations Point mutations (transitions vs transversions) Structural Gene Mutations (silent, missense, nonsense, frameshift) Supressor mutations (intragenic vs intergenic) vs Reverse mutations Spontaneous mutations (DNA replication, depurination of purines, deamination of cytosines, tautomeric shifts) Induced Mutagens Chemical (base modifiers, base analogues, intercalating agents) Physical (Ionizing radiation very potent – able to break bonds; non-ionizing radiation such as UV causing thymine dimmers) Ames Test Repair mechanisms (methyl-directed mismatch repair, photolyase removal of thymine dimers caused by UV irradiation; Xeroderma pigementosum is caused by the lack of a repair mechanism) Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Transcriptional regulation Repressors/ activators Catabolic regulation uses induction= Positive control (lac operon) Anabolic regulation uses repression =Negative control (trp operon) Inducers, Corepressors, Inhibitors Lac Operon (a polycistronic mRNA)[Positive control regulation] Promoter, Operator, CAP site, lac Z (B-galactosidase), lac Y (permease) and the lac I (repressor) regulation by repressor (inducer is allolactose) regulation by activator protein (CAP plus the inducer cAMP) Induction in the presence of Glucose and/or Lactose Trp Operon (another polycistronic mRNA) [negative control] trp R is the repressor protein; corepressor is trypotophan itself (feed-back regulator) Attenuation (coupled transcription & translation allows for tryptophan to feedback and cause premature termination of transcript) Translational Regulation (inhibitors that prevent translation) Antisense RNA Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Transcription factors and regulatory elements Chromatin compaction changes DNA Methylation (expression, repair, imprinting & disorders) Alternative splicing Stability of mRNA BIO 184 Laboratory CSU, Sacramento Fall 2008 Meiosis and Mitosis Chromosomes vs chromatids Homologous chromosomes Non-disjunction Chromosome number variations (genome mutations) Euploidy (variation of complete sets) Polyploidy Aneuploidy (variation of particular chromosomes within a set) Sex Chromosomes vs Autosomes Natural Mechanisms to Produce Chromosome Number Variations Meiotic Nondisjunction (difference between nondisjuction in meiosis 1 vs 2) New Species Formation (autopolyploid, allopolyploid) X-inactivation (Barr bodies) Chromosome Structure & Recombination (rearrangements) Types of Mutations that Alter Chromosome Structure Deletions/Defiencies (pseudodominance) Duplications (creation of gene families) Inversions (pericentric, paracentric, inversion heterozygotes) Translocations (reciprocal, simple or unbalanced; meiotic segregation of ` can lead to balanced or unbalanced gametes) Familial Down Syndrome