Genetic Disorders
advertisement

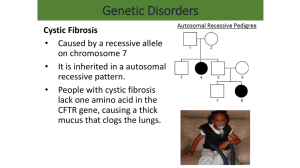
Genetic Disorders & Chromosomal Mutations Chapter 12 Karyotype Karyotype: picture of homologous chromosomes arranged in pairs Human = 46 chromos. = 23 pairs Sex chromosomes = determine sex of human (1 pair) • Male: XY • Female: XX Autosomes = all others (22 pairs) Pedigree Chart Shows relationships within a family Each row is a different generation Males: ■ Females: ● Vertical: children; Horizontal: couples Solid shape: has trait Used to track appearance of traits Can infer genotype of family members Recessive Allele Disorders Revealed only when dominant allele is absent Disorders: 1) PKU (phenylketonuria): newborns lack enzyme to break down phenylaline in milk → severe mental retardation 2) Tay-Sachs: nervous system breakdown → death by age 4 • Mostly central and eastern Europeans PKU Tay Sachs Recessive Allele Disorders 3) Cystic Fibrosis: Causes respiratory and digestive problems Most common fatal genetic disorder 4) Sickle Cell Disease: Results in bent and twisted red blood cells; ↓ blood O2 levels Causes physical weakness; brain, heart, and spleen damage; death Closely linked to malaria Cystic Fibrosis Sickle Cell Disease Dominant Allele Disorders Always revealed (even if recessive allele is present) Disorders: 1) Acondroplasia: type of dwarfism 2) Huntington’s disease: progressive loss of muscle and mental functioning • No symptoms until in 30’s Mutations Mutation: any change in DNA May involve entire chromosome or single nucleotide May take place in ANY cell May be beneficial or deadly (“lethal”) Occur in 2 types of cells: • Germ-Cell Mutation: occur in gametes (sex cells); passed on to children • Somatic Mutation: occur in body cells Chromosome Mutations Non-Disjunction: failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis Results in gain/loss of entire chromosome Trisomy 21: inheritance of extra chromos. #21 • “Down Syndrome” Karyotype of Trisomy 21 Chromosome Mutations 1) Deletion: loss of piece of chromosome Chromosome Mutations 3) Translocation: swapping segments of nonhomologous chromosomes