Krafts_Pituitary_Path_FINAL
advertisement

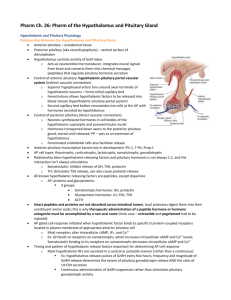
Krafts – Pituitary Path – 2.5.10 Anterior Pituitary •GH, ACTH, TSH, LH, FSH, and prolactin. •Controlled by hypothalamus horms. Most stim release of ant pit horm except dopamine which inhibits prolactin secretion. •Most problems happen here. Acidophils GH PL “B FLAT” Basophils FSH LH ACTH TSH Hypopituitary S/Sx: ↓ GH Kid: pituitary dwarfism Adult: muscle weakness ↓ FSH/LH loss of libido menstrual abnorm loss of body hair ↓ PL inability to lactate ↓ TSH 2nd Hypothyroidism ↓ ACTH adrenal insufficiency Posterior Pituitary -extension of hypothalamus stores oxytocin & ADH. •Oxytocin: labor, milk let-down, cuddling (after orgasm), monogamy (vole studies), trust (investment experiment). Changes don’t cause Sx unless preg or nursing -ADH (vasopressin) •Hypothalamus makes them Posterior pituitary stores them 1 Hyperpituitarism: Too much anterior pituitary hormone(s) Causes •pituitary adenoma (table pg 2) •destruction of end organs •hypothalamic disorders •hyperplasia of anterior lobe •carcinoma of anterior lobe Posterior pituitary syndromes -- ADH Diabetes Insipidus Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion Hypopituitarism Too little anterior pituitary hormone(s) Causes •Pituitary destruction •Ischemic necrosis •Empty sella syndrome •Pituitary apoplexy •Hypothalamic lesions Clinical: not always clear Sx •Insidious, chronic •One or two hormones •Panhypopituitarism rare •GH, then FSH/LH, TSH, ACTH Cause •Central (ADH deficency) or nephrogenic (kidney prob) • ADH •Pee dilute urine – kidney cant conc urine •Serum Na & osmolality increases brain effects •cause: Head trauma, tumors, alcohol consumption •Increase water intake Urine tastes bland (unlike diabetes mellitus) Tx: inc water intake, give ADH • ADH •Retain water -- very conc urine •Blood becomes hypotonic •Usually mild, sometimes bad •Ectopic ADH production (small-cell lung CA) •Tx: Decrease water intake 2 Krafts – Pituitary Path – 2.5.10 Cause pituitary adenomas GENERAL Clinical •None, for a while! •Endocrine abnormalities (sometimes) •Mass effects •visual deficits1 •increased intracranial pressure •HYPOpit –if big enough & non secreting it can compress the normal pit dec Epidemiology •Common •Adults •MEN I (multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes – hereditary) -TSH –secreting is least common -Autopsy (30%) Molecular: •Mutated GNAS1 gene (mutant G protein) •Mutated MEN-1 gene •Mutated RAS, c-MYC genes (activating mutation) Path •Within sella or beyond •1 cm •“Invasive” – bengin tumor don’t invade, but if they get big enough they can press into the surrounding tissue •Can bleed suddenly (emergency) Micropath •Sheets/cords •Uniform cells of one type (acidophil etc) •May have pleomorphic nuclei •May have mitoses •Can’t tell type w/o immunohistochemical stain -great variation! (image of it will not be on exam) Prolactinoma •Commonest type of pituitary adenoma •Efficient secretion •Amenorrhea, galactorrhea •Other things can increase prolactin! Stalk effect = disruption of hypothalamic input to pit inc prolactin •Can treat with dopamine receptor agonists (bromocriptine) Other adenoma’s Tx by surgery Growth Hormone Adenoma Gigantism •Pre-pubertal adenoma •Very tall •Very very long arms, legs ACTH Adenoma4 FSH/LH adenoma Other manifestations of GH adenoma: •Diabetes mellitus •Hypertension •Arthritis •Gastrointestinal carcinoma Dx Labs: • GH (spurts throughout day) • IGF-I (better) •GH unresponsive to glucose (should dec) Tx: surgery & radiation to get GH back to normal Acromegaly •Post-pubertal adenoma •Very tall •Enlarged bones of face (frontal bossing, big jaw, coarse facial features) hands •Makes ACTH (from POMC) POMC ACTH, MSH, endorphin •Cushing syndrome (too much cortisol for many dif causes. Sx = glucose intolerant, buffalo hump, moon facies) •Cushing disease (special cushing syn w/ACTH adenoma) •Nelson syndrome – if you remove the adrenal gland, you will lose inhibit effects on cortisol uncontrolled pit adenoma growth •Inefficient •Gets big 3 Krafts – Pituitary Path – 2.5.10 1. bilateral hemianopsia – missing sight in lateral fields on both sides from the pit tumor pressing on the optic nerve. 3. 2. know this chart! There is too big grps of molecules that cancer. Some molecules (red) make the cells grow. If you have a genetic abnormality that turns one of these on all the time neoplasia (cancer) uncontrolled growth. Things that inhibit growth (blue) things that stop cell cycle at certain pts to check DNA. If you screw up those genes then it is like taking the breaks off. Some of these are affected in pituitary ademona – RAS (looks like it is always on)! (which gene?) mutation makes it always on – when it binds to recp the GDP falls off & GTP falls on stim adenyl cyclase. w/adenoma it can get turned off, it can lose the extra phosphate. 4. exogenous ingestion is the most common. Paraenoplastic – tumor in lung makes something that looks like ACTH & the adrenal response to it w/cortisol. 4 Krafts – Pituitary Path – 2.5.10 Types Pituitary Destruction Cause •Big pituitary adenoma •Surgery or radiation Ischemic Necrosis (Sheehan’s syndrome) •Pituitary gets BIG, blood flow stays same (pregnancy is the most common cause) •Hemorrhage (delivery) causes hypotension •Pituitary (already hypoxic) becomes necrotic Empty Sella Syndrome •Arachnoid, CSF herniation takes up space Pituitary compression •Usually NO hypopituitarism! Pituitary Apoplexy •Sudden infarction of adenoma •Meningeal symptoms •Can be deadly Hypothalamic Lesions •Tumors, infections •Rare! Path Questions: 1. What happens to pituitary hormone output if you cut off hypothalamic input? 2. What’s apoplexy? 3. Sponge Bob,why is panhypopituitarism so rare? Answer: 1. prolactin all other hormones 2. apoplexy (greek apoplexia, to strike down, disable by a stroke): sudden paralysis with loss of consciousness and sensation, caused by the damaging of blood vessels in the brain. 3. Why, Clucky, it’s because the pituitary has such a big reserve!