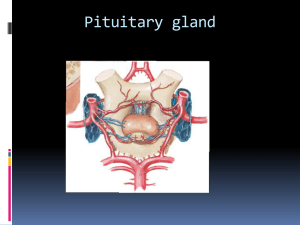
handout

Cushing’s, Addison’s and Acromegaly
Cushing’s
Syndrome: excessive activation of glucocorticoid receptors.
Disease: excessive ACTH due to pituitary adenoma.
Classification:
ACTH-dependent pituitary adenoma, ectopic ACTH, iatrogenic.
ACTH-independent iatrogenic, adrenal adenoma/carcinoma.
Pseudo-Cushing’s EtOH excess, major depressive disorder, 1 obesity
Clinical features: hair thinning, hirsuitism, psychosis, acne, plethora, cataracts, mild exophthalmos, moon face, peptic ulcers, vertebral #, hypertension, hyperglycaemia, central adiposity, menstrual disturbance, striae, decreased skin thickness, osteoporosis, proximal myopathy, infections, poor wound healing, bruising, impaired immune response.
Investigations:
Bedside cap glucose, BP.
Bloods dexamethasone suppression test, CRH test, serum cortisol.
Imaging MRI brain, CXR, CT AP/adrenals.
Others inferior venous petrosal sampling, urinary free cortisol.
Management:
Conservative patient education, reduce oral steroid therapy if possible.
Medical ketoconazole/metyrapone ( steroid synthesis).
Surgical trans-sphenoidal resection of pituitary.
Addison’s
Definition: a syndrome resulting from inadequate secretion of corticosteroid hormones from progressive destruction of the adrenal cortex.
Causes: “ADDISON” – Autoimmune, Degenerative, Drugs, Infective, Secondary,
Other, Neoplasia.
Clinical features: bronze pigmentation of skin, tiredness, hypoglycaemia, postural hypotension, changes in distribution of body hair, weight loss, GI disturbance. Associated with type 1 diabetes, pernicious anaemia, autoimmune thyroid disease and vitiligo.
Investigations:
Bedside lying/standing BP, capillary glucose.
Bloods U&Es, synacthen test, plasma renin, aldosterone, HIV test.
Imaging AXR, CT/MRI adrenals.
Management:
Glucocorticoid replacement – hydrocortisone BD.
Mineralocorticoid replacement – fludrocortisone OD.
Addisonian crisis (shock, hypotension, abdo pain, N&V, Na + / K + ) –
ABCDE, correct volume depletion, replace glucocorticoids, correct metabolic abnormalities, treat underlying cause.
Acromegaly
Definition: a condition caused by excessive growth hormone secretion.
Causes: most commonly, pituitary adenoma.
Clinical features: headache, skull growth (prominent supraorbital ridge with large frontal sinuses), enlargement of lips, nose and tongue, prognathism, cardiomyopathy, increased sweating, thickened skin, hepatomegaly, type 2 diabetes, enlargement of hands, carpal tunnel syndrome, myopathy, enlargement of feet, visual field changes, diplopia.
Investigations:
Bedside collateral hx, serial photographs, BP, ECG.
Bloods serum GH, OGTT, serum IGF-1.
Imaging CT/MRI brain, echo.
Other colonoscopy.
Management:
Conservative patient education.
Medical (second line) somatostatin analogues (octreotide, lanreotide), dopamine agonists, GH receptor anatagonists (pegvisomant).
Surgery (first line) trans-sphenoidal debulking of tumour.
Radiotherapy if acromegaly persists after surgery.




![Anti-ARA9 antibody [1B6] ab131577 Product datasheet 2 Images Overview](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012691684_1-14586210b76104388b5cf4eeef189e95-300x300.png)