At the Clinic Scenario: Endocrine System
advertisement

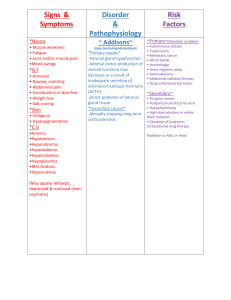
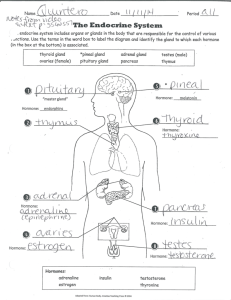
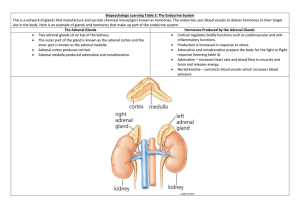
Kim, Frances Period 1 Bertha Wise, age 40, comes to the clinic, troubled by swelling in her face and unusual fat deposition on her back and abdomen. She reports that she bruises easily. Blood tests show elevated glucose levels. What is your diagnosis and what glands might be causing the problem? In addition to the adrenal glands in cushings, the pituitary often plays a part. Pituitary Tumor ACTH Test Corticosteroids Cushing Syndrome Multiple Symmetric Lipomatosis LEVEL B ACTH Adrenal Gland Tiny organs that rest on top of each kidney. Plays an important role in the body, it produces numerous hormones that impact our development and growth. Affects our ability to deal with stress and helps regulate kidney function. Two Parts of Adrenal Gland Adrenal Cortex: Produces cortisol, a hormone that regulates nearly every type of organ and tissue within the body. Also produces aldosterone. It helps to maintain appropriate proportions of water and salts within the body. Results in low blood pressure. Cushing Syndrome Results of the excessive production of corticosteroids by the adrenal glands. SYMPTOMS: change in body habitus, weight gain in the face, above the collar bone and on the back of the neck, skin changes with easy bruising, excess hair growth on the face, etc. CAUSES: can develop by taking glucocorticoids or their body is exposed to high levels of cortisol. Glucocorticoids are steroid hormones that are chemically similar to the cortisol produced by our bodies. TREATMENTS Varies and depends on the cause of cortisol excess. Adrenal Gland Scars CT is the primary imaging method. ACTH Adrenocorticotropic Hormone A.K.A. : corticotropin Polypeptide tropic hormone Pituitary Gland Pea sized gland located at the base of the skull between the optic nerves. Controls temperature, growth during childhood, urine production, testosterone production (in males) & ovulation & estrogen production in females. Pituitary Tumor Abnormal growths that develop in your pituitary glands. • SYMPTOMS: Headache, vision loss, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, weakness, constipation, and etc. TREATMENTS: Depends on its size and how far it has grown into your brain. Age and overall health are factors. Involves a brain surgeon, endocrine system specialist and a nervous system specialist.