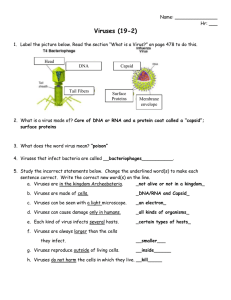
Viruses What is a virus? Non Living Microscopic organism Need
advertisement

Viruses What is a virus? Non Living Microscopic organism Need host cell to reproduce (hijacks the cell and has it make more viruses) What is a virus made of? Made of DNA or RNA and a capsid (coat made of protein) Many contain an envelope (membrane surrounding the capsid) which helps them enter cells The capsid is made of protein, lipid and glycoproteins (protein + carbohydrate molecule) How do viruses spread? Person to person or Mother to child Contact, exchange of saliva/coughing/sneezing, contaminated food/water, insects (Endocytosis) Remember: Bacteriophages! (Virus that infects bacteria) Lytic Cycle: (1) Virus attaches to a cell and injects DNA (2) viral DNA enters the lytic cycle (3) new virus is made (4) cell breaks open and releases viruses Lysogenic Cycle: (1) Virus attaches to a cell and injects DNA (2) viral DNA enters the lysogenic cycle (3) Viral DNA integrates with host DNA (4) Host cell divides normally (5) virus may enter lytic cycle **single virus that infects a bacterial cell can produce 100 new viruses in 20 minutes** Diseases caused by viruses Common cold, smallpox, measles, chickenpox, flu, HPV, polio, HIV, herpes, Epstein-Barr (mono) Tobacco Mosaic Virus How do we fight viruses? Healthy immune system, skin integrity, hand washing Sometimes we vaccinate (flu or smallpox) Sometimes we can give anti-viral medication Smallpox disease was eliminated in 1970’s after an effort to inoculate every man, woman, and child in the world. Two collections of frozen smallpox virus have been preserved, one in Atlanta and the other in Moscow. Why? Research in case of bioterrorism Prions and Viroids Prion: 1982 – described by Stanley Prusiner at Stanford University Made of protein, but have no nucleic acid. Disease causing prions are folded in a way that doesn’t allow the protein to function, contact with normal proteins causes them to misfold and stop functioning. (Chain reaction) (1) Scrapie – sheep (2) Mad Cow Disease – cow (3) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease – humans Viriod: single strand of RNA with no capsid Important infectious disease agents in plants (cucumbers, oranges, potatoes, avocado)