Ch10 Reproduction
advertisement

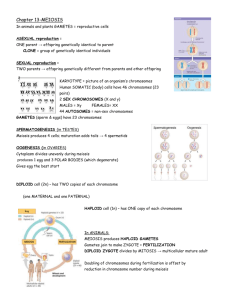
Ch10 Reproduction True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 1. A gamete has one-half the number of chromosomes of a regular body cell. ____ 2. Homologous chromosomes are two chromosomes with identical DNA sequences. ____ 3. Recent research suggests that beneficial mutations accumulate faster when species undergo sexual reproduction rather than asexual reproduction. ____ 4. During meiosis, chromosome number is reduced through three rounds of cell division. ____ 5. Sexual reproduction would be more advantageous than asexual reproduction for organisms living in an environment that is diverse and undergoes frequent changes. ____ 6. Mendel’s work on garden pea plants resulted in the discovery that genetic traits of parents always blend together in subsequent generations. ____ 7. In humans, the ability to roll one’s tongue is a dominant trait. Therefore, a tongue roller can only have children who are also tongue rollers. ____ 8. The separation of genes during crossing over occurs more frequently between genes that are far apart on a chromosome than for genes that are close together. ____ 9. One map unit between two genes indicates that crossing over occurs between them 100 percent of the time. ____ 10. Polyploidy is more common in plants than animals. ____ 11. Polyploid plants such as coffee and strawberries are often less healthy and smaller than diploid plants of the same species. ____ 12. During meiosis I, homologus chromosome pairs are separated when the centromeres split apart. ____ 13. Meiosis occurs during both sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. ____ 14. Gregor Mendel’s research supports the idea each organism carries a pair of alleles. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 15. The numbers in Figure 10-1 represent the chromosome number found in each of the dog cells shown. The processes that are occurring at A and B are ____. Figure 10-1 a. mitosis and fertilization b. meiosis and fertilization c. mitosis and pollination d. meiosis and pollination ____ 16. A white mouse whose parents are both white produces only brown offspring when mated with a brown mouse. The white mouse is most probably ____. a. homozygous recessive c. homozygous dominant b. heterozygous d. haploid ____ 17. In chickens, rose comb (R) is dominant to single comb (r). A homozygous rose-combed rooster is mated with a single-combed hen. All of the chicks in the F1 generation were kept together as a group for several years. They were allowed to mate only within their own group. What is the expected phenotype of the F2 chicks? a. 100% rose comb b. 75% rose comb and 25% single comb c. 100% single comb d. 50% rose comb and 50% single comb ____ 18. In mink, brown fur color is dominant to silver-blue fur color. If a homozygous brown mink is mated with a silver-blue mink and 8 offspring are produced, how many would be expected to be silver-blue? a. 0 c. 6 b. 3 d. 8 ____ 19. The diagram in Figure 10-2 shows a diploid cell with two homologous pairs of chromosomes. Due to independent assortment, the possible allelic combinations that could be found in gametes produced by the meiotic division of this cell are ____. Figure 10-2 a. Bb, Dd, BB, and DD c. BbDd and BDbd b. BD, bD, Bd, and bd d. Bd and bD only ____ 20. Using Figure 10-3, which process would result in the formation of chromosome C from chromosomes A and B? Figure 10-3 a. asexual reproduction c. crossing over b. independent assortment d. segregation ____ 21. Which event during meiosis leads to a reduction in chromosome number from 2n to n? a. Pairs of homologous chromosomes line up at the equator. b. DNA undergoes replication. c. Homologous chromosomes travel to opposite sides of the cell. d. Sister chromatids are pulled apart at the centromere. ____ 22. Crossing over would most likely occur during which stage of the cell cycle? a. when DNA is being replicated b. when homologous chromomosomes line up in pairs ____ 23. ____ 24. ____ 25. ____ 26. ____ 27. ____ 28. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. ____ 33. c. when centromeres are separated d. when cytokinesis begins Which is the best description of the events that take place during anaphase II? a. The replicated chromosomes become visible. b. Homologous chromosomes line up along the equator. c. Sister chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite sides of the cell. d. Homologous pairs are separated and pulled to opposite sides of the cell. What is the role of the spindle fibers? a. to join homologous chromosomes together b. to store nucleotides prior to DNA synthesis c. to initiate the formation of the nuclear membrane d. to move chromosomes in the cell The typical human body cell contains 46 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are found in a typical human sperm? a. 23 c. 46 b. 45 d. 92 During which phase of meiosis do homologous pairs of chromosomes line up next to one another along the equator? a. anaphase I c. prophase II b. metaphase I d. metaphase II Which stage of meiosis is responsible for the law of independent assortment? a. metaphase I c. telophase I b. prophase I d. metaphase II A true-breeding tall pea plant is crossed with a true-breeding short pea plant, and all the offspring are tall. What is the most likely genotype of the offspring assuming a single-gene trait? a. tt c. TT b. Tt d. TT or tt Mendel took the pollen from a tall pea plant and pollinated the flower of a short pea plant. When he did this, he removed the male parts of the flower on the short plant. Why was it important that he remove the male parts from the flower of the short plant? a. because he wanted to prevent self pollination b. because the short plant was heterozygous c. because he wanted to prevent the development of seeds d. because the short plant was not a true-breeding plant A heterozygous organism is best described as which of these? a. dominant c. hybrid b. genotype d. true-breeding In which situation are the phenotypes of F2 offspring expected to follow the ratio of 9:3:3:1. a. a monohybrid cross for 2 unlinked traits b. a monohybrid cross for 2 closely linked traits c. a dihybrid cross for 2 unlinked traits d. a dihybrid cross for 2 closely linked traits If two heterozygous individuals are crossed, what percent of their offspring are also expected to be heterozygous? a. 0 c. 75 b. 50 d. 100 Of the following species used in agriculture, which is most likely a polyploid? a. cow c. hen b. goat d. wheat Figure 10-9 ____ 34. Consider the cell labeled X in Figure 10-9 containing 4 chromosomes. Which of the four cells below it represents a healthy gamete that could be produced from this cell? a. A c. C b. B d. D