Study Guide Answers: Cellular Reproduction Bio
advertisement

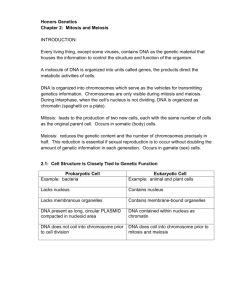
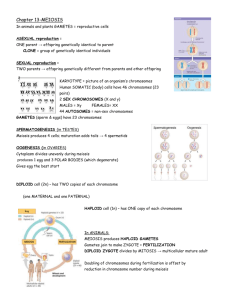
Study Guide Answers: Cell Reproduction 1. DNA is first copied. Then the cell divides into equal halves by adding new cell membrane between two DNA copies. The growing cell membrane pushes inward, the cell constricts to form two new, identical cells. A new cell wall forms around each new membrane. 2. A diploid gamete would result if the nondisjunction affected all the chromosomes during one of the meiotic divisions. 3. A haploid cell (n) contains one set of chromosomes. A diploid cell (2n) contains two sets of chromosomes. 4. Crossing over creates recombinant chromosomes having a combination of genes that were originally on different, though homologous, chromosomes. Homologous chromosome pairs are oriented randomly at metaphase of meiosis I. 5. Karyotype of a Down syndrome person has more than two copies of a chromosome called Trisomy whereas a normal karyotype only has two copies of a chromosome. 6. G1 phase – cell grows rapidly and carries out routine functions; G2 phase – preparations are made for the nucleus to divide, microtubules are assembled; S phase – DNA is copied 7. Chromosomes condense right before a cell divides in mitosis. During most of interphase chromosomes are not condensed and are harder to see with a microscope. 8. An organism with more than two sets of homologous chromosomes in its genome. 9. In mitosis, the duplication of chromosomes is followed by one division of the cell. In meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate in the first of two cell divisions; after second division, each new cell ends up with just a single haploid set. 10. In plant cells, vesicles formed by the Golgi apparatus fuse at the equator and form the cell plate. A new cell wall forms on both sides of the plate. In animal cells, the cell is pinched in half by a belt of protein threads.