File
advertisement

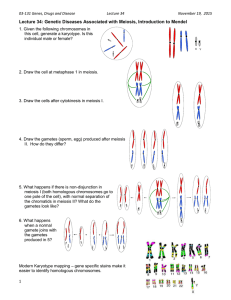
Study Guide for AP Biology Test 3 Chapters 9-11 Chapter 9 Mitosis Cell cycle o Order- G1, S, G2 and G0 for those that never divide o What happens in each stage? o What controls the cell cycle? Checkpoints Growth factors Density-dependent inhibition Anchorage dependence o What happens if a cell becomes unregulated? Tumors Benign Malignant Metastasis o Mitosis How many chromosomes in each stage using specific example Stages: PMAT- don’t worry about prometaphase Cytokinesis Cleavage furrow Cell plate End product Chromatids- joined copies of the original chromosome Centromere, kinetochore, mitotic spindle, centrioles, centrosomes o What happens in prokaryotes instead of mitosis? Binary fission DNA form o Eukaryotic vs. prokaryotic o Chromosome, chromatin Somatic cells vs. gametes Chapter 10 Meiosis Reductional division Somatic cells vs. gametes Locus, gene, allele Asexual reproduction vs. sexual reproduction- what are the advantages of each (see 10.4) Homologous chromosomes Karyotype o What are they used for? o Could you identify an issue of a human karyotype? o What is nondisjunction? Sex chromosomes and autosomes Fertilization and zygote Meiosis o Homologous chromosomes bond together (synapsis) and cross over during prophase I. What is crossing over? Haploid vs. diploid (which type of cell does meiosis produce?) Two rounds of division-homologous pairs split up first, then sister chromatids~ meiosis I and meiosis II Genetic variation o Independent assortment- (yes-this is getting at the same point as in Ch. 11) o Crossing over o Random fertilization Chapter 11 Character Trait True-breeding Hybridization P, F1, F2 Monohybrid cross and Punnett square Dihybrid cross and Punnett square Probability math and be able to solve trihybrid cross o Multiplication rule o Addition rule Homozygous Heterozygous Phenotype Genotype Dominant Recessive Law of segregation and law of independent assortment Testcross o Why important? o How is it done? Codominance- blood groups Incomplete dominance Pleiotropy Epistasis Multiple alleles Polygenic inheritance- ex. height Environmental impact on phenotype o Be able to explain how the environment can affect a phenotype Ex. In high-sun environment, skin would be tan. Why are recessive alleles still around? Why aren’t dominant alleles always the most common? o Dominant disorders, natural selection Pedigrees o Be able to explain o Carriers (heterozygous)