Bellwork #23 Genetic Diversity
advertisement

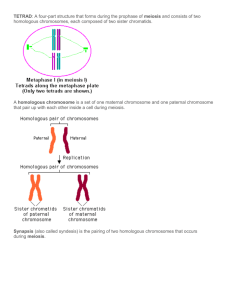
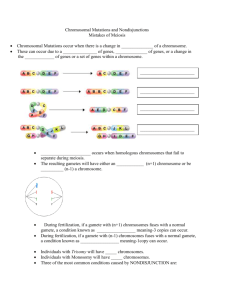
Bellwork #23 Genetic Diversity Cells that are formed by 1 __________ are identical to each other and to the parent cell. Conversely, 2 ________ increases genetic diversity because every sperm or egg is a little bit different. No two offspring are exactly the same. Genetic diversity causes some organisms to be more fit to survive and reproduce. Genetic diversity is essential for the 3 ______________ of species. With very little gene variation within the species, healthy reproduction becomes increasingly difficult. Crossing over during meiosis allows recombination of genes between 4 ___________ chromosomes. This alters the linkage between genes on the same chromosome. Crossing over occurs frequently during 5 _______________ of meiosis, when homologous chromosomes associate with each other in a structure called a 6 ___________. Recall that one member of each pair of 7 ___________ chromosomes came from one parent, and the other member came from the other parent. Without crossing over, each 8 ____________ cell produced will inherit a chromosome with the same combination of genes as was on one of the parental chromosomes. Crossing over is important because it results in new 9 _________________ of genes that are different from either parent, contributing to genetic diversity. During 10 ____________, the homologous chromosomes line up 11 _______________ in the middle of the cell. Therefore, there is a 12 ____% chance of the maternal or paternal chromosomes going to either side of the cell. 13 ______________________ is the process where chromosomes randomly segregate towards either side of the cell during 14 ______________ of meiosis resulting in the production of genetically unique 15 ________________. 16 _____________ is an error in meiosis when homologous chromosomes fail to separate properly during 17 ____________ or one 18 ___________ fail to separate in anaphase II. Recall that during meiosis I, one chromosome from each 19 ___________ pair moves to each pole of the cell. In nondisjunction, both chromosomes of a homologous pair move to the same pole of the cell. Nondisjunction will result in two kinds of 20 ___________. One gamete will have an extra chromosome, and the other gamete is missing a chromosome. For example, when a gamete with an extra chromosome is fertilized by a normal gamete, the 21 ________will have an extra chromosome. This condition is called 22 ________. In humans, if a gamete with an extra chromosome number 21 is fertilized by a normal gamete, the resulting 23 ______has 24 ____ chromosomes instead of 25 ____. This zygote will develop into a baby with 26 ________________. _______________________________________________ WORD BANK__________________________________________________ a. 46 b. 47 c. 50 d. combinations e. evolution f. gametes (x2) g. haploid h. homologous (x3) i. anaphase I (x2) j. nondisjunction k. tetrad l. metaphase I m. mitosis n. meiosis o. chromatid p. prophase I q. zygote (x2) r. randomly s. trisomy t. Down syndrome u. independent assortment