Study Guide - Genetics Quiz
advertisement
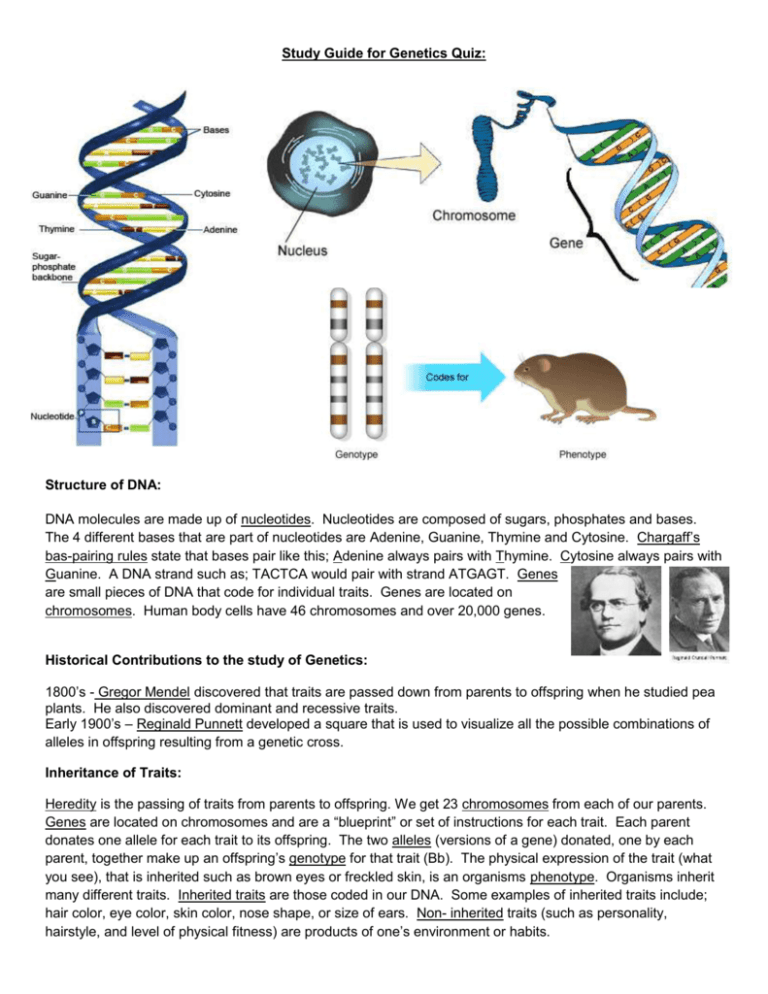
Study Guide for Genetics Quiz: Structure of DNA: DNA molecules are made up of nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of sugars, phosphates and bases. The 4 different bases that are part of nucleotides are Adenine, Guanine, Thymine and Cytosine. Chargaff’s bas-pairing rules state that bases pair like this; Adenine always pairs with Thymine. Cytosine always pairs with Guanine. A DNA strand such as; TACTCA would pair with strand ATGAGT. Genes are small pieces of DNA that code for individual traits. Genes are located on chromosomes. Human body cells have 46 chromosomes and over 20,000 genes. Historical Contributions to the study of Genetics: 1800’s - Gregor Mendel discovered that traits are passed down from parents to offspring when he studied pea plants. He also discovered dominant and recessive traits. Early 1900’s – Reginald Punnett developed a square that is used to visualize all the possible combinations of alleles in offspring resulting from a genetic cross. Inheritance of Traits: Heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring. We get 23 chromosomes from each of our parents. Genes are located on chromosomes and are a “blueprint” or set of instructions for each trait. Each parent donates one allele for each trait to its offspring. The two alleles (versions of a gene) donated, one by each parent, together make up an offspring’s genotype for that trait (Bb). The physical expression of the trait (what you see), that is inherited such as brown eyes or freckled skin, is an organisms phenotype. Organisms inherit many different traits. Inherited traits are those coded in our DNA. Some examples of inherited traits include; hair color, eye color, skin color, nose shape, or size of ears. Non- inherited traits (such as personality, hairstyle, and level of physical fitness) are products of one’s environment or habits. Alleles (different versions of a gene) can be either dominant or recessive. In genetics, dominant genes are represented by capital letters (B), and recessive genes are represented by lowercase letters (b). A dominant gene will always show through if it is present (BB, Bb). A recessive trait cannot appear unless two recessive alleles (bb) are inherited. See picture below. Most of the genetics examples we use in 7th grade science are like this. Example: Brown eyes are dominant to blue eyes. Probability is the mathematical chance that an event will occur. Punnett Squares are used to show the probability that offspring (babies) will inherit different traits, based on their parents’ genotypes. Each box represents a 25% chance of offspring inheriting that combination of alleles. Gene: Eye color Alleles: Brown (B) and blue (b) Homozygous / Purebred - Genotypes that have two of the same alleles: dominant (BB) or recessive (bb). Heterozygous / Hybrid– Genotypes that include 2 different alleles, (Dd). The dominant allele shows. *Example Punnett Square Problem: Two brown eyed parents are both heterozygous for that trait. What are the chances that they will have a child with blue eyes? B B b Genotypic Ratio is: b BB Bb Bb bb 1 : 2: 1 BB Bb bb Phenotypic Ratio is: ___3__ : ___1__ Dominant : Recessive Chance of child having blue eyes: 25% Mitosis vs. Meiosis: Mitosis Mitosis – Division of the nucleus and DNA in eukaryotic body cells. In humans, body cells each have 46 chromosomes. Before mitosis, the DNA is copied (92 chromosomes) and then the DNA is divided through mitosis, resulting in two identical daughter cells, each with 46 chromosomes. Meiosis – Production of eukaryotic sex cells. In humans, meiosis results in the creation of egg and sperms. Egg and sperm cells each have 23 chromosomes (a random combination of the individual’s genes). This ensures that the offspring will have 46 chromosomes, a random combination of ½ of mother and ½ of father’s genes. This is why two siblings (brothers and sisters) can look very similar or very different. Meiosis









