Frequently Asked Questions - Cedarville Elementary RTI/Progress
advertisement

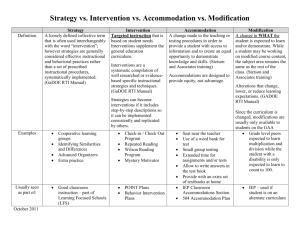
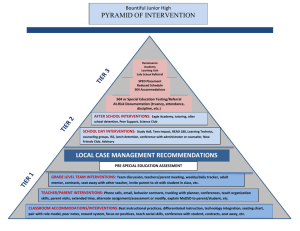
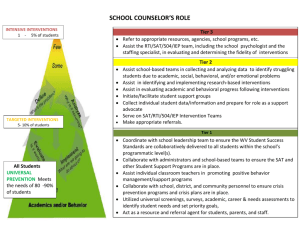
RTI Frequently Asked Questions Interventions What are some examples of interventions? An intervention is a scientifically based instruction targeting a specific deficit. Using that definition, interventions may be specific programs targeting a specific area of concern (ie.- Moby Max, Earobics), a specific strategy targeting a specific area of concern (ie.- Repeated Readings, Incremental Rehearsal, etc.). Specific interventions are on the website for teacher reference. How do we organize individual interventions in the classroom without tutors? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Centers Parent Volunteers Peer Tutors (High School students) Differentiated Instruction Individual within class short-term intervention sessions Self-monitoring techniques How does an intervention work pre-RTI/post-RTI? Do we try interventions before RTI? Interventions can happen before, during, and after RTI. Interventions should be done for four to six weeks, at least three times per week. It is necessary to document these interventions, and the student’s response to the intervention. Examples of how to collect data, and recording instruments are available on the website. When can a student be tested for a disability? When interventions are not being successful and the gap is not closing and the student is well below grade-level in the case of a suspected Specific Learning Disability or suspected Intellectual Disability. In the case of behaviors that interfere with performance, there must be interventions in place to address the behaviors before a disability can be considered. How long are students going to stay in the RTI process? When the gap has closed to the point that the student is no longer struggling in class, or the student has been identified as having a Specific Learning Disability or other Intellectual Disability. Are self-directed computer programs interventions? Yes, if they are research-based and can collect data. Are parents using flash-cards considered an intervention? The responsibility for interventions falls solely on the school, and not on the parents. Accommodations What are accommodations? Accommodations make the same curriculum accessible to all. Examples are preferential seating, extended time, voice amplification systems, breaks, etc. It is providing the same curriculum to the student that all other students receive, but it allows them to have more opportunities for success where there are deficits. If students are really struggling, do we start with accommodations first for them to feel more successful? Yes, but be able to provide performance data with and without the accommodation provided. Can, or do accommodations overlap with modifications? Yes, sometimes they can. For example, extended time can be an accommodation when time is not a factor, but it is a modification on a timed test. Do students not on an IEP or 504 receive accommodations? All students may receive accommodations. When do you start accommodations? As soon as you notice a need arise, however, collect data based on student performance with and without an accommodation. When do we contact parents to let them know we are making accommodations? Immediately upon starting the accommodations. When would it be appropriate to move from an intervention to an accommodation? Accommodations typically become before interventions. Modifications What is a modification? Modifications are “changes” to the curriculum. For example, reduced expectations (ie.- reduced spelling lists, one paragraph instead of two, lower level reading/math materials, etc.), changing the grading system, and a different means of assessment (ie.—oral responses on tests, oral report instead of written, etc.). When is it okay to give a modification? Do students have to have an IEP or 504? Typically, modifications are given to students on a 504 and IEP. Don’t confuse modifications with differentiation. Differentiation is encouraged. Do we document modifications on report cards? Modifications for IEPs and 504s are communicated through progress reports. Modifications provided through RTI should be communicated to parents immediately. At what point do you modify work during the RTI process? Following the RTI team’s recommendation, however this is not likely to be the case. When should parents be contacted? Parents will be contacted through the RTI and IEP/504 process. How do I know when to start taking modifications away? This is a team decision (RTI or IEP/504). This decision is made based on student success. Differentiation What is differentiation? Differentiation is meeting the different needs of students through personalized instruction. This may be done through small groups, varied assignments, extending standards, independent studies. Students are still accountable for grade-level standards. Is it differentiation to reduce problems, but from each section? This is a modification. Please consult the above section for more details.