Chapters 8 and 11 Study Guide
advertisement

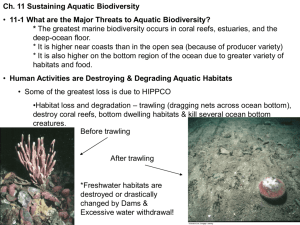
AP Environmental Science Name_________________________ Chapters 8 and 11 Study Guide 8-1 What is the general nature of aquatic systems? 1. What services (both ecological and economic) do coral reefs provide? 2. Globally, ___________% of reefs have been destroyed and another ____________% have been degraded. An additional ________________% could be lost in the coming decades. 3. What is degradation? 4. Saltwater and freshwater aquatic zones cover approximately how much of the earth’s surface? 5. What determines the major types of organisms found in an aquatic environment? 6. There are four major types of organisms in aquatic systems. Describe and give examples of each: A. Plankton B. Nekton C. Benthos D. Decomposers 7. What is primary productivity? 8. What percentage of primary productivity near the ocean surface can be attributed to ultraplankton? 9. In aquatic systems, what are the four key factors that determine the types and numbers of organisms present? A. B. C. D. 10. Where does photosynthesis largely take place in aquatic ecosystems? 11. What can be limiting factors of photosynthesis in aquatic systems? AP Environmental Science Name_________________________ 8-2 Why are marine aquatic systems important? 12. What are the two major life zones of the oceans?. A. B. 13. Which zone is most affected by human activities? 14. Coastal zone ecosystems constitute __________% of the oceans and contain ____________% of all marine species. 15. Describe characteristics of the coastal zone including sunlight, nutrient availability, location, and services provided to the environment: 16. What is an estuary? 17. What is a mangrove forest, and where do we find them? 18. What are some ways organisms in the intertidal zone have adapted to the conditions there? 19. What are barrier islands? 20. Coral reefs are home to _______________ of all marine species. 21. The open sea is divided into three vertical zones based primarily on penetration of light. Describe characteristics of each zone and its organisms: A. The euphotic zone B. The bathyal zone C. The abyssal zone 8-3 How have human activities affected marine ecosystems? 22. What percentage of the world’s ocean area have been heavily affected by human activities? 23. What percentage of the global population lives along coasts? Is that figure expected to rise or fall? AP Environmental Science 24. What are the 7 major threats to marine systems? A. Name_________________________ B. C. D. E. F. G. H. 8-4 Why are freshwater ecosystems important? 25. Describe lentic and lotic systems and give examples of each. A. Lentic B. Lotic 26. In what ways can lakes receive water? 27. Describe each of the four zones of a lake: A. Littoral zone B. limnetic zone C. Profundal zone D. Benthic zone 28. What are the differences between an oligotrophic, mesotrophic, and eutrophic lake? 29. What is surface water? 30. What is runoff? AP Environmental Science 31. What is a watershed? Name_________________________ 32. There are three aquatic life zones along a stream, each with different conditions, describe each: A. source zone B. transition zone C. floodplain zone 33. What is causing the shrinking of many deltas? 34. Why the shrinking of the deltas significant to the city of New Orleans? 35. What is a wetland? 36. What are some examples of wetlands? 37. What ecosystem services do wetlands provide? 8-5 How have human activities affected freshwater ecosystems? 38. What four human activities have major impacts on freshwater systems? A. B. C. D. 39. What has happened to the majority of the inland wetlands in the United States? AP Environmental Science Name_________________________ Chapter 11 11-1 What are the major threats to aquatic biodiversity? 40. How has the International Whaling Commission attempted to regulate the whaling industry? 41. What countries are still whaling today? 42. Why do we know very little about the aquatic biodiversity? 43. Where does the greatest marine biodiversity occur? 44. Why is biodiversity higher near the coasts? 45. Where is biodiversity higher, the bottom region or the surface region of the ocean? 46. What is the greatest threat to the biodiversity of oceans? 47. Why are dredging and trawling a major threat to the sea floor habitats? 48. What is an invasive species? 49. How have invasive species impacted marine biodiversity? 50. What has led to the extinction of the various species of cichlids in Lake Victoria? 51. How have carp had a negative impact on Lake Wingara? 52. By 2020, _____________% of the world’s population will live near coasts. 53. What are some of the pollutants affecting ocean systems? What affect is each having? AP Environmental Science Name_________________________ 54. How is climate change threatening aquatic biodiversity and ecosystems services? 55. What is overfishing? 56. What is sustainable yield? 57. Global fishing is taking _____________% more than sustainable yield. 58. What is commercial extinction? 59. What can happen if numbers in predatory species begin to dwindle? 60. Describe each type of industrial fishing technique: A. Trawler fishing B. Purse-seine fishing C. Longlining D. drift netting 61. ______________% of marine species and _________________% of freshwater species may face extinction within the next 60-70 years. 11-2 How can we protect and sustain marine biodiversity? 62. Why is protecting marine biodiversity so challenging? 63. Describe each of the following national and international laws and treaties that deal with aquatic ecosystems: A. CITES B. 1979 Global Treaty on Migratory Species C. US Marine Mammal Protection Act AP Environmental Science D. Endangered Species Act Name_________________________ E. US Whale Conservation and Protection Act F. International Convention on Biological Diversity 64. How many species of marine turtles are endangered? 65. What human activities are responsible for their endangerment? 66. What is being done in trawler fishing to help reduce the number of sea turtles caught in nets? 67. A country’s offshore fishing zone extends ________________ kilometers from its shores. 68. What is the Exclusive Economic Zone? 69. What are marine protected areas (MPA’s)? 70. How many MPA’s exist? 71. What harmful human activities can still take place in most MPA’s? 72. How are scientists proposing we take an “ecosystem approach” to sustaining marine biodiversity? 73. Less than _________% of the world’s ocean area is closed to fishing in marine reserves. 74. What is reconciliation ecology? How can it be used to help these ecosystems? 75. What is integrated coastal management? 11-3 How should we manage and sustain marine fisheries? 76. What is maximum sustained yield? 77. What are the reasons maximum sustained yield has likely aided in the collapse of most commercially valuable fish stocks? AP Environmental Science 78. What is optimum sustained yield? Name_________________________ 79. What is multi-species management? 80. What is the precautionary principle? 81. What roles do the communities and government play in the management of local fisheries? 82. What is quota? 83. How are government subsidies actually harming the management of fisheries? 84. What are individual transfer rights (ITRs)? 85. What can an individual do to help sustain aquatic diversity? 11-4 How should we protect and sustain wetlands? 86. Despite their value, the U.S. has lost more than __________________ of its coastal and inland wetlands since 1900. 87. Why will loss of wetlands increase as global warming leads to rising sea levels? 88. Pertaining to wetlands, what is the “zero net loss” goal of the U.S. Government? 89. What is mitigation banking? 90. Briefly describe the restoration project being proposed for the Florida Everglades: 11-5 How can we protect and sustain freshwater lakes, rivers, and fisheries? 91. How many invasive species have entered the great lakes since the 1920’s? 92. Describe the effects of a few of these invasive species: AP Environmental Science 93. How can rivers and streams be degraded? Name_________________________ 94. How many dams are on the Columbia River? 95. Describe the National Wild and Scenic Rivers Act? 96. In 2009, Congress increased the total length of wild and scenic rivers by _____________. Still, less than _________% of the country’s total river length is protected. 11-6 What should be our priorities for sustaining aquatic biodiversity? 97. How can we reverse the harmful effects of human activities on our aquatic biodiversity?